-
40 Publicações
-
8 fotos
-
2 Vídeos
-
Trading na Ikeja
-
Reside em Lagos, Nigeria
-
De Ikeja
-
Estudou Bsc, Accounting na Logos State University, Ojo
-
Seguido por 81 pessoas
Atualizações Recentes
-
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - (Please Read &Share)
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS):
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. It's characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries.
Symptoms:
1. Irregular periods or amenorrhea (no periods)
2. Weight gain and obesity
3. Acne and skin issues
4. Excess hair growth on face, chest, and back
5. Male pattern baldness
6. Fertility issues
Causes and Risk Factors:
1. Hormonal imbalance
2. Genetics
3. Insulin resistance
Management and Treatment:
1. Hormonal birth control to regulate periods
2. Anti-androgen medications for acne and hair growth
3. Fertility medications for women trying to conceive
4. Lifestyle changes: healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management
Importance of Early Diagnosis:
Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce risk of long-term complications like diabetes and heart disease.
Here are some additional points about PCOS:
Complications:
1. Infertility: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in women.
2. Metabolic Syndrome: Increased risk of developing diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
3. Mental Health: Women with PCOS are at higher risk of depression, anxiety, and eating disorders.
Lifestyle Changes:
1. Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and avoid sugary and high-carbohydrate foods.
2. Exercise: Regular physical activity can help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce symptoms.
3. Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and anxiety.
Support:
1. Support Groups: Joining a support group can connect you with others who understand what you're going through.
2. Online Resources: There are many online resources and forums dedicated to PCOS, where you can find information, support, and community.
Remember to:
1. Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your symptoms and adjust treatment plans as needed.
2. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about PCOS, its symptoms, and treatment options.
If you're experiencing symptoms or have concerns about PCOS, don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Let's break the stigma surrounding PCOS and prioritize our health!
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - (Please Read &Share) POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS): What is PCOS? Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. It's characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. Symptoms: 1. Irregular periods or amenorrhea (no periods) 2. Weight gain and obesity 3. Acne and skin issues 4. Excess hair growth on face, chest, and back 5. Male pattern baldness 6. Fertility issues Causes and Risk Factors: 1. Hormonal imbalance 2. Genetics 3. Insulin resistance Management and Treatment: 1. Hormonal birth control to regulate periods 2. Anti-androgen medications for acne and hair growth 3. Fertility medications for women trying to conceive 4. Lifestyle changes: healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce risk of long-term complications like diabetes and heart disease. Here are some additional points about PCOS: Complications: 1. Infertility: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility in women. 2. Metabolic Syndrome: Increased risk of developing diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. 3. Mental Health: Women with PCOS are at higher risk of depression, anxiety, and eating disorders. Lifestyle Changes: 1. Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and avoid sugary and high-carbohydrate foods. 2. Exercise: Regular physical activity can help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce symptoms. 3. Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and anxiety. Support: 1. Support Groups: Joining a support group can connect you with others who understand what you're going through. 2. Online Resources: There are many online resources and forums dedicated to PCOS, where you can find information, support, and community. Remember to: 1. Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular health check-ups can help monitor your symptoms and adjust treatment plans as needed. 2. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about PCOS, its symptoms, and treatment options. If you're experiencing symptoms or have concerns about PCOS, don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Let's break the stigma surrounding PCOS and prioritize our health!0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 86 Visualizações 0 AnteriorFaça Login para curtir, compartilhar e comentar! -
TALK FOR THE TODAY (Please Read &Share)
8+8+8 RULES TO BALANCE LIFE
The 8+8+8 rule offers a balanced approach to managing daily life. By allocating time into three 8-hour blocks, individuals can prioritize:
1. Work (8 hours): Focus on professional or personal projects, ensuring productivity and career growth.
2. Good Sleep (8 hours): Prioritize rest and rejuvenation for physical and mental health.
3. Personal Time (8 hours): Divide this into three aspects:
- 3F - Family, Friends, and Faith: Strengthen relationships, nurture connections, and explore spirituality.
- 3H - Health, Hygiene, and Hobbies: Maintain physical well-being, practice self-care, and enjoy personal interests.
- 3S - Soul, Service, and Smile: Cultivate inner peace, engage in community service, and spread positivity.
This framework encourages:
- Balance: Allocate time effectively across different areas of life.
- Self-care: Prioritize physical, emotional, and mental well-being.
- Relationships: Nurture connections with loved ones and build meaningful relationships.
- Personal growth: Pursue hobbies, interests, and spiritual growth.
By embracing the 8+8+8 rule, individuals can create a more balanced, fulfilling, and purposeful life.TALK FOR THE TODAY (Please Read &Share) 8+8+8 RULES TO BALANCE LIFE The 8+8+8 rule offers a balanced approach to managing daily life. By allocating time into three 8-hour blocks, individuals can prioritize: 1. Work (8 hours): Focus on professional or personal projects, ensuring productivity and career growth. 2. Good Sleep (8 hours): Prioritize rest and rejuvenation for physical and mental health. 3. Personal Time (8 hours): Divide this into three aspects: - 3F - Family, Friends, and Faith: Strengthen relationships, nurture connections, and explore spirituality. - 3H - Health, Hygiene, and Hobbies: Maintain physical well-being, practice self-care, and enjoy personal interests. - 3S - Soul, Service, and Smile: Cultivate inner peace, engage in community service, and spread positivity. This framework encourages: - Balance: Allocate time effectively across different areas of life. - Self-care: Prioritize physical, emotional, and mental well-being. - Relationships: Nurture connections with loved ones and build meaningful relationships. - Personal growth: Pursue hobbies, interests, and spiritual growth. By embracing the 8+8+8 rule, individuals can create a more balanced, fulfilling, and purposeful life.0 Comentários 1 Compartilhamentos 159 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
Health Talk for Today ANORECTAL (please read & share.
Anorectal refers to the region of the body that includes the anus and rectum. This area is part of the digestive system and plays a crucial role in eliminating waste.
Some common anorectal conditions include:
1. Hemorrhoids
2. Anal fissures
3. Anal abscesses
4. Rectal prolapse
5. Anal cancer
Symptoms may include:
1. Pain or discomfort
2. Bleeding
3. Itching
4. Swelling
5. Difficulty with bowel movements
Maintaining good anorectal health is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some tips:
1. Practice good hygiene: Keep the anal area clean.
2. Eat a high-fiber diet: Prevent constipation.
3. Stay hydrated: Softens stool.
4. Avoid straining: During bowel movements.
5. Exercise regularly: Improves digestion.
Common issues:
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal fissures
- Constipation
If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professionalHealth Talk for Today ANORECTAL (please read & share. Anorectal refers to the region of the body that includes the anus and rectum. This area is part of the digestive system and plays a crucial role in eliminating waste. Some common anorectal conditions include: 1. Hemorrhoids 2. Anal fissures 3. Anal abscesses 4. Rectal prolapse 5. Anal cancer Symptoms may include: 1. Pain or discomfort 2. Bleeding 3. Itching 4. Swelling 5. Difficulty with bowel movements Maintaining good anorectal health is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some tips: 1. Practice good hygiene: Keep the anal area clean. 2. Eat a high-fiber diet: Prevent constipation. 3. Stay hydrated: Softens stool. 4. Avoid straining: During bowel movements. 5. Exercise regularly: Improves digestion. Common issues: - Hemorrhoids - Anal fissures - Constipation If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 156 Visualizações 0 Anterior2
-
HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY - COLON CANCER (Pleas and Sha)
Colon Cancer: Understanding the Risks and Symptoms
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, occurs when cells in the colon or rectum grow out of control, forming a tumor.
Risk Factors
1. *Age*: Risk increases with age, especially after 50.
2. *Family History*: A family history of colon cancer or polyps increases risk.
3. *Genetic Syndromes*: Certain genetic syndromes, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or Lynch syndrome.
4. *Diet*: A diet high in red meat and low in fiber may increase risk.
5. *Obesity*: Being overweight or obese may increase risk.
Symptoms
1. *Blood in Stool*: Blood in or on the stool, or black, tarry stools.
2. *Changes in Bowel Habits*: Diarrhea, constipation, or narrow stools.
3. *Abdominal Pain*: Abdominal pain or cramping.
4. *Weakness or Fatigue*: Feeling weak or tired.
5. *Unexplained Weight Loss*: Losing weight without trying.
Screening and Diagnosis
1. *Colonoscopy*: A procedure that examines the entire colon.
2. *Stool Tests*: Tests that check for blood or DNA in stool.
3. *Imaging Tests*: Tests such as CT scans or MRI scans.
Treatment
1. *Surgery*: Surgery to remove the tumor and affected tissue.
2. *Chemotherapy*: Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells.
3. *Radiation Therapy*: Radiation therapy to kill cancer cells.
Prevention
1. *Screening*: Regular screening can help detect colon cancer early.
2. *Healthy Diet*: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
3. *Exercise*: Engaging in regular physical activity.
Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. If you're 50 or older, talk to your doctor about screening options.
Colon Cancer: Additional Information
Types of Colon Cancer
1. *Adenocarcinoma*: The most common type, arising from glandular cells.
2. *Carcinoid tumors*: Rare, slow-growing tumors.
3. *Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs)*: Rare tumors.
Stages of Colon Cancer
1. *Stage I*: Cancer is limited to the colon or rectum.
2. *Stage II*: Cancer has grown through the wall of the colon or rectum.
3. *Stage III*: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
4. *Stage IV*: Cancer has spread to distant organs.
Treatment Options
1. *Surgical resection*: Removing the tumor and affected tissue.
2. *Chemotherapy*: Killing cancer cells with medication.
3. *Targeted therapy*: Targeting specific cancer cells or proteins.
4. *Immunotherapy*: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer.
Lifestyle Changes
1. *Diet*: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
2. *Exercise*: Engaging in regular physical activity.
3. *Weight management*: Maintaining a healthy weight.
4. *Smoking cessation*: Quitting smoking.
Importance of Screening
1. *Early detection*: Screening can detect colon cancer at an early stage.
2. *Prevention*: Screening can help prevent colon cancer by removing precancerous polyps.
If you have concerns about colon cancer or screening, consult with your healthcare provider.HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY - COLON CANCER (Pleas and Sha) Colon Cancer: Understanding the Risks and Symptoms Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, occurs when cells in the colon or rectum grow out of control, forming a tumor. Risk Factors 1. *Age*: Risk increases with age, especially after 50. 2. *Family History*: A family history of colon cancer or polyps increases risk. 3. *Genetic Syndromes*: Certain genetic syndromes, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or Lynch syndrome. 4. *Diet*: A diet high in red meat and low in fiber may increase risk. 5. *Obesity*: Being overweight or obese may increase risk. Symptoms 1. *Blood in Stool*: Blood in or on the stool, or black, tarry stools. 2. *Changes in Bowel Habits*: Diarrhea, constipation, or narrow stools. 3. *Abdominal Pain*: Abdominal pain or cramping. 4. *Weakness or Fatigue*: Feeling weak or tired. 5. *Unexplained Weight Loss*: Losing weight without trying. Screening and Diagnosis 1. *Colonoscopy*: A procedure that examines the entire colon. 2. *Stool Tests*: Tests that check for blood or DNA in stool. 3. *Imaging Tests*: Tests such as CT scans or MRI scans. Treatment 1. *Surgery*: Surgery to remove the tumor and affected tissue. 2. *Chemotherapy*: Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells. 3. *Radiation Therapy*: Radiation therapy to kill cancer cells. Prevention 1. *Screening*: Regular screening can help detect colon cancer early. 2. *Healthy Diet*: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. 3. *Exercise*: Engaging in regular physical activity. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. If you're 50 or older, talk to your doctor about screening options. Colon Cancer: Additional Information Types of Colon Cancer 1. *Adenocarcinoma*: The most common type, arising from glandular cells. 2. *Carcinoid tumors*: Rare, slow-growing tumors. 3. *Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs)*: Rare tumors. Stages of Colon Cancer 1. *Stage I*: Cancer is limited to the colon or rectum. 2. *Stage II*: Cancer has grown through the wall of the colon or rectum. 3. *Stage III*: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. 4. *Stage IV*: Cancer has spread to distant organs. Treatment Options 1. *Surgical resection*: Removing the tumor and affected tissue. 2. *Chemotherapy*: Killing cancer cells with medication. 3. *Targeted therapy*: Targeting specific cancer cells or proteins. 4. *Immunotherapy*: Boosting the immune system to fight cancer. Lifestyle Changes 1. *Diet*: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. 2. *Exercise*: Engaging in regular physical activity. 3. *Weight management*: Maintaining a healthy weight. 4. *Smoking cessation*: Quitting smoking. Importance of Screening 1. *Early detection*: Screening can detect colon cancer at an early stage. 2. *Prevention*: Screening can help prevent colon cancer by removing precancerous polyps. If you have concerns about colon cancer or screening, consult with your healthcare provider.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 247 Visualizações 0 Anterior1
-
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - EFFECT OF ABSTAINING FROM SEX - MEN (Please Read &Share)
Abstaining from sex for a long time can have various effects on physical and mental health, though these can vary widely among individuals. Some potential effects include:
1. *Buildup of sexual tension*: This can lead to discomfort or frustration.
2. *Decreased libido*: Temporary reduction in sex drive might occur.
3. *Sperm quality issues*: In men, prolonged abstinence might affect sperm quality.
4. *Stress and anxiety*: Some people might experience increased stress or anxiety.
5. *Sleep disturbances*: Changes in sexual activity can sometimes impact sleep patterns.
6. *Potential impact on prostate health*: Some studies suggest that regular ejaculation might help reduce the risk of prostate issues, though this is still
Additional potential effects of prolonged sexual abstinence in men may include:
1. *Erectile dysfunction*: Some studies suggest a possible link between infrequent sexual activity and erectile dysfunction.
2. *Testicular discomfort*: Some men might experience testicular discomfort or pain due to prolonged sexual arousal without release.
3. *Mood changes*: Hormonal changes or unfulfilled sexual needs might affect mood.
4. *Social and relationship impacts*: Prolonged abstinence can strain relationships or affect social interactions.
5. *Prostate health debates*: Some research suggests potential benefits of regular ejaculation for prostate health, but more research is needed.
Individual experiences vary, and not all men will experience these effects. If concerns arise, consulting a healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance.HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - EFFECT OF ABSTAINING FROM SEX - MEN (Please Read &Share) Abstaining from sex for a long time can have various effects on physical and mental health, though these can vary widely among individuals. Some potential effects include: 1. *Buildup of sexual tension*: This can lead to discomfort or frustration. 2. *Decreased libido*: Temporary reduction in sex drive might occur. 3. *Sperm quality issues*: In men, prolonged abstinence might affect sperm quality. 4. *Stress and anxiety*: Some people might experience increased stress or anxiety. 5. *Sleep disturbances*: Changes in sexual activity can sometimes impact sleep patterns. 6. *Potential impact on prostate health*: Some studies suggest that regular ejaculation might help reduce the risk of prostate issues, though this is still Additional potential effects of prolonged sexual abstinence in men may include: 1. *Erectile dysfunction*: Some studies suggest a possible link between infrequent sexual activity and erectile dysfunction. 2. *Testicular discomfort*: Some men might experience testicular discomfort or pain due to prolonged sexual arousal without release. 3. *Mood changes*: Hormonal changes or unfulfilled sexual needs might affect mood. 4. *Social and relationship impacts*: Prolonged abstinence can strain relationships or affect social interactions. 5. *Prostate health debates*: Some research suggests potential benefits of regular ejaculation for prostate health, but more research is needed. Individual experiences vary, and not all men will experience these effects. If concerns arise, consulting a healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 261 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – FIBROID (Please Read & Share)
Part 2 of 2
Fibroids and Fertility
Fibroids can affect fertility in several ways:
Interference with ovulation: Fibroids can interfere with ovulation, making it harder to conceive. Implantation issues: Fibroids can affect the lining of the uterus, making it harder for a fertilized egg to implant.
Miscarriage: Fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage.
Fibroids and Pregnancy
Fibroids can also affect pregnancy in several ways:
Preterm labor: Fibroids can increase the risk of preterm labor.
Fetal growth restriction: Fibroids can affect fetal growth and development.
Cesarean delivery: Women with fibroids may be more likely to require a cesarean delivery.
Managing Fibroids During Pregnancy
If you have fibroids and become pregnant, your healthcare provider may recommend:
Regular monitoring: Regular ultrasounds and check-ups to monitor fibroid growth and fetal development.
Pain management: Medications or other treatments to manage pain and discomfort.
Bed rest: In some cases, bed rest may be recommended to reduce the risk of preterm labor.
Fibroids and Menopause
Fibroids often shrink after menopause, but some women may still experience symptoms. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may affect fibroid growth, so it's essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Fibroids and Lifestyle
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can help manage fibroid symptoms:
Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce symptoms and improve overall health.
Stress management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help manage stress.
Conclusion
Fibroids are a common health issue for women, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, symptoms can be managed and quality of life improved. If you're experiencing symptoms or concerns, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – FIBROID (Please Read & Share) Part 2 of 2 Fibroids and Fertility Fibroids can affect fertility in several ways: Interference with ovulation: Fibroids can interfere with ovulation, making it harder to conceive. Implantation issues: Fibroids can affect the lining of the uterus, making it harder for a fertilized egg to implant. Miscarriage: Fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage. Fibroids and Pregnancy Fibroids can also affect pregnancy in several ways: Preterm labor: Fibroids can increase the risk of preterm labor. Fetal growth restriction: Fibroids can affect fetal growth and development. Cesarean delivery: Women with fibroids may be more likely to require a cesarean delivery. Managing Fibroids During Pregnancy If you have fibroids and become pregnant, your healthcare provider may recommend: Regular monitoring: Regular ultrasounds and check-ups to monitor fibroid growth and fetal development. Pain management: Medications or other treatments to manage pain and discomfort. Bed rest: In some cases, bed rest may be recommended to reduce the risk of preterm labor. Fibroids and Menopause Fibroids often shrink after menopause, but some women may still experience symptoms. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may affect fibroid growth, so it's essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider. Fibroids and Lifestyle In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can help manage fibroid symptoms: Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce symptoms and improve overall health. Stress management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help manage stress. Conclusion Fibroids are a common health issue for women, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, symptoms can be managed and quality of life improved. If you're experiencing symptoms or concerns, consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 381 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – FIBROIDS (Please Read & Share)
Part 1 of 2
Understanding Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyoma’s, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. These growths can vary in size, shape, and location, and are common in women of reproductive age. While many women with fibroids may not experience symptoms, others may face heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility issues.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, but research suggests that hormonal influences, genetics, and environmental factors may contribute to their development. Women between the ages of 30 and 50 are more likely to develop fibroids, and those with a family history are at higher risk.
Symptoms
Fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding or prolonged menstrual periods
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Infertility or miscarriage
Diagnosis
Diagnosing fibroids typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and medical history. A pelvic exam can help identify abnormalities in the uterus, while imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can confirm the presence of fibroids.
Treatment Options
Treatment for fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the growths, and the woman's reproductive goals. Options include:
- Watchful waiting: Monitoring symptoms and fibroid growth over time
- Medications: Hormonal therapies to shrink fibroids or manage symptoms
- Surgery: Myomectomy (removing fibroids) or hysterectomy (removing the uterus)
- Minimally invasive procedures: Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery
Lifestyle Changes
While fibroids can't be prevented, lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing stress
To be continue
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – FIBROIDS (Please Read & Share) Part 1 of 2 Understanding Fibroids: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyoma’s, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. These growths can vary in size, shape, and location, and are common in women of reproductive age. While many women with fibroids may not experience symptoms, others may face heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility issues. Causes and Risk Factors The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, but research suggests that hormonal influences, genetics, and environmental factors may contribute to their development. Women between the ages of 30 and 50 are more likely to develop fibroids, and those with a family history are at higher risk. Symptoms Fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, including: - Heavy menstrual bleeding or prolonged menstrual periods - Pelvic pain or pressure - Frequent urination - Constipation - Infertility or miscarriage Diagnosis Diagnosing fibroids typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and medical history. A pelvic exam can help identify abnormalities in the uterus, while imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can confirm the presence of fibroids. Treatment Options Treatment for fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the growths, and the woman's reproductive goals. Options include: - Watchful waiting: Monitoring symptoms and fibroid growth over time - Medications: Hormonal therapies to shrink fibroids or manage symptoms - Surgery: Myomectomy (removing fibroids) or hysterectomy (removing the uterus) - Minimally invasive procedures: Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery Lifestyle Changes While fibroids can't be prevented, lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms. These include: - Maintaining a healthy weight - Exercising regularly - Eating a balanced diet - Managing stress To be continue0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 271 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – OVARIAN CANCER (Please Read & Share)
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility.
What are the ovaries?
The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They have two main functions:
1. Egg production: The ovaries produce eggs (oocytes) that are released during ovulation.
2. Hormone production: The ovaries produce hormones like estrogen and progesterone that regulate the menstrual cycle, fertility, and female reproductive health.
How does ovarian cancer develop?
Ovarian cancer develops when abnormal cells in the ovaries grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Over time, these cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body.
What are the types of ovarian cancer?
There are several types of ovarian cancer, including:
1. Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases. It develops from the outer layer of the ovary.
2. Germ cell ovarian cancer: This type is rare and develops from the cells that produce eggs.
3. Stromal ovarian cancer: This type is also rare and develops from the connective tissue of the ovary.
What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer?
Several factors can increase a woman's risk of developing ovarian cancer, including:
1. Family history: Having a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) with ovarian cancer increases risk.
2. Genetic mutations: Inherited mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly increase risk.
3. Age: Ovarian cancer risk increases with age, especially after 50.
4. Reproductive history: Women who have never had children or have a history of infertility may be at higher risk.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer symptoms can be vague and similar to other conditions. Common symptoms include:
1. Abdominal bloating or swelling
2. Pelvic pain or pressure
3. Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
4. Urinary frequency or urgency
5. Fatigue or weight loss
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosing ovarian cancer can be challenging, but common methods include:
1. Pelvic exam: A doctor performs a physical exam to check for abnormalities.
2. Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the ovaries.
3. Blood tests: CA-125 test to measure protein levels, which can be elevated in ovarian cancer.
4. Biopsy: Surgical removal of tissue for examination.
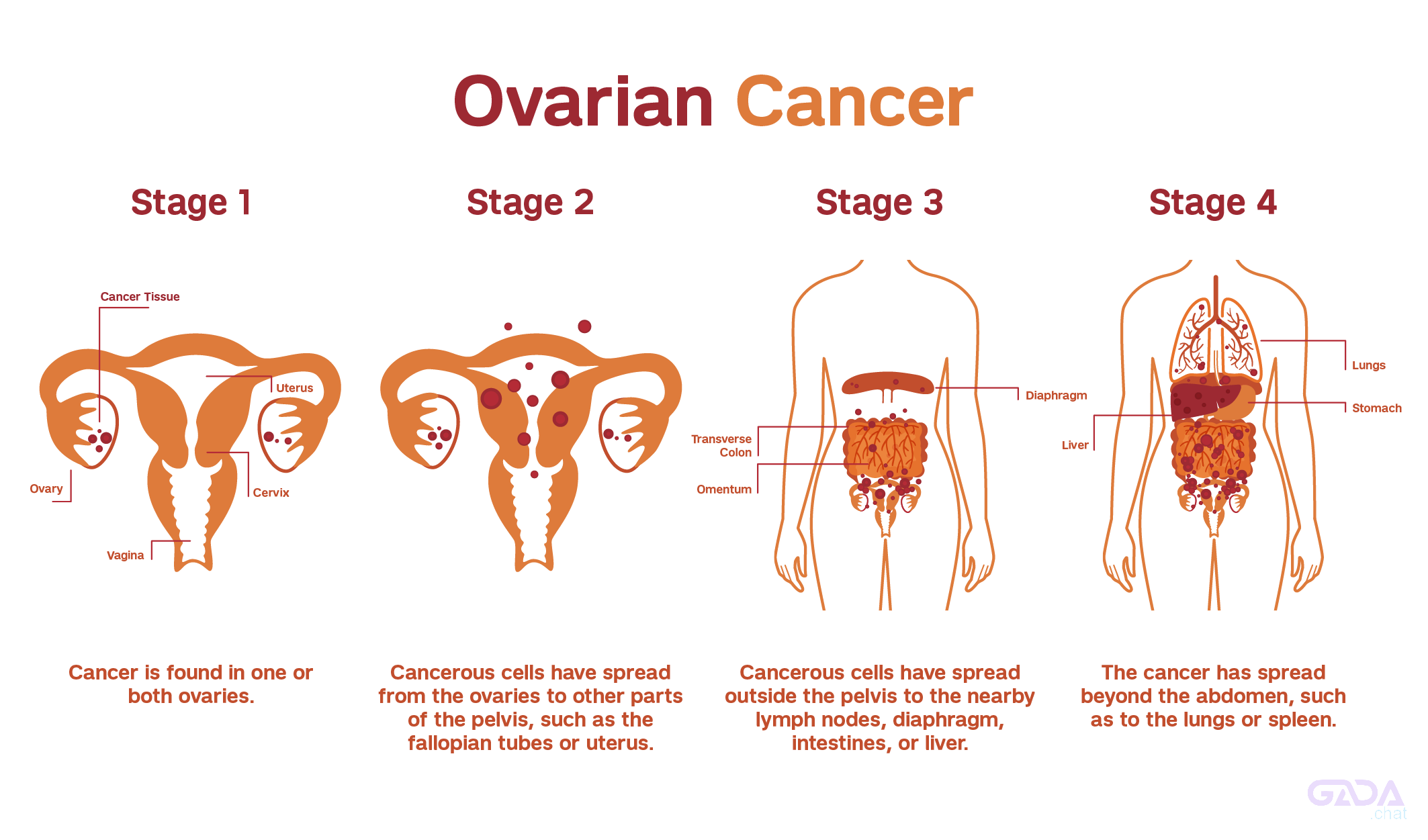
What are the stages of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is staged based on its spread:
1. Stage I: Cancer is limited to the ovaries.
2. Stage II: Cancer has spread to the pelvis.
3. Stage III: Cancer has spread to the abdomen or lymph nodes.
4. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs.
What are the treatment options?
Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer:
Surgical Approaches
Surgery is the first step in treating ovarian cancer. Minimally invasive surgical techniques may be appropriate for certain patients.
The goal of surgery is to remove as many cancerous cells as possible. Surgical options include:
• Salpingo-oophorectomy is the surgical removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
• Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix.
• Debulking is the surgical removal of any additional cancerous cells and tumors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancerous cells. To limit side effects and damage to healthy cells, ovarian cancer patients are usually given chemotherapy in cycles with several rest periods. Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery, or both.
Most women receive intravenous chemotherapy (injected into a vein). Our expert gynecologic oncologists determine the most effective combination of drugs for each patient, depending on a variety of factors.
Hormone Therapy
Some types of ovarian cancers can be treated with hormone therapy. This treatment blocks receptors and inhibits female hormones to prevent ovarian cancer cells from getting or using the hormones needed to grow and multiply. Hormone therapy is usually given in the form of pills.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is the use of medications to stimulate your immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. Your physician determines the best immunotherapy medications and timing for taking them.
With care from a highly trained gynecologic oncologist, immunotherapy can be an integral part of your ovarian cancer treatment.
Targeted therapy: Treatments that target specific cancer cell proteins.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – OVARIAN CANCER (Please Read & Share) Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. What are the ovaries? The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They have two main functions: 1. Egg production: The ovaries produce eggs (oocytes) that are released during ovulation. 2. Hormone production: The ovaries produce hormones like estrogen and progesterone that regulate the menstrual cycle, fertility, and female reproductive health. How does ovarian cancer develop? Ovarian cancer develops when abnormal cells in the ovaries grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Over time, these cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. What are the types of ovarian cancer? There are several types of ovarian cancer, including: 1. Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases. It develops from the outer layer of the ovary. 2. Germ cell ovarian cancer: This type is rare and develops from the cells that produce eggs. 3. Stromal ovarian cancer: This type is also rare and develops from the connective tissue of the ovary. What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer? Several factors can increase a woman's risk of developing ovarian cancer, including: 1. Family history: Having a first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) with ovarian cancer increases risk. 2. Genetic mutations: Inherited mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly increase risk. 3. Age: Ovarian cancer risk increases with age, especially after 50. 4. Reproductive history: Women who have never had children or have a history of infertility may be at higher risk. What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer symptoms can be vague and similar to other conditions. Common symptoms include: 1. Abdominal bloating or swelling 2. Pelvic pain or pressure 3. Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly 4. Urinary frequency or urgency 5. Fatigue or weight loss How is ovarian cancer diagnosed? Diagnosing ovarian cancer can be challenging, but common methods include: 1. Pelvic exam: A doctor performs a physical exam to check for abnormalities. 2. Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the ovaries. 3. Blood tests: CA-125 test to measure protein levels, which can be elevated in ovarian cancer. 4. Biopsy: Surgical removal of tissue for examination. What are the stages of ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is staged based on its spread: 1. Stage I: Cancer is limited to the ovaries. 2. Stage II: Cancer has spread to the pelvis. 3. Stage III: Cancer has spread to the abdomen or lymph nodes. 4. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs. What are the treatment options? Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer: Surgical Approaches Surgery is the first step in treating ovarian cancer. Minimally invasive surgical techniques may be appropriate for certain patients. The goal of surgery is to remove as many cancerous cells as possible. Surgical options include: • Salpingo-oophorectomy is the surgical removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. • Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. • Debulking is the surgical removal of any additional cancerous cells and tumors. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancerous cells. To limit side effects and damage to healthy cells, ovarian cancer patients are usually given chemotherapy in cycles with several rest periods. Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery, or both. Most women receive intravenous chemotherapy (injected into a vein). Our expert gynecologic oncologists determine the most effective combination of drugs for each patient, depending on a variety of factors. Hormone Therapy Some types of ovarian cancers can be treated with hormone therapy. This treatment blocks receptors and inhibits female hormones to prevent ovarian cancer cells from getting or using the hormones needed to grow and multiply. Hormone therapy is usually given in the form of pills. Immunotherapy Immunotherapy is the use of medications to stimulate your immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. Your physician determines the best immunotherapy medications and timing for taking them. With care from a highly trained gynecologic oncologist, immunotherapy can be an integral part of your ovarian cancer treatment. Targeted therapy: Treatments that target specific cancer cell proteins.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 267 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAT – BREAST CANCER (Please Read & Share)
Breast Cancer Awareness
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the breast tissue. It's one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
Key Facts:
1. Risk Factors: Family history, genetics, age, radiation exposure, and hormonal factors.
2. Symptoms: Lump or thickening in the breast, change in breast shape or size, nipple discharge or pain.
3. Screening: Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams.
4. Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Prevention and Early Detection:
1. Get screened regularly
2. Know your breast health
3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight)
4. Be aware of family history
Types of Breast Cancer:
1. Invasive ductal carcinoma: Begins in milk ducts and spreads to surrounding tissue.
2. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Starts in lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads.
3. Triple-negative breast cancer: Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors.
4. HER2-positive breast cancer: Has an overexpression of HER2 protein.
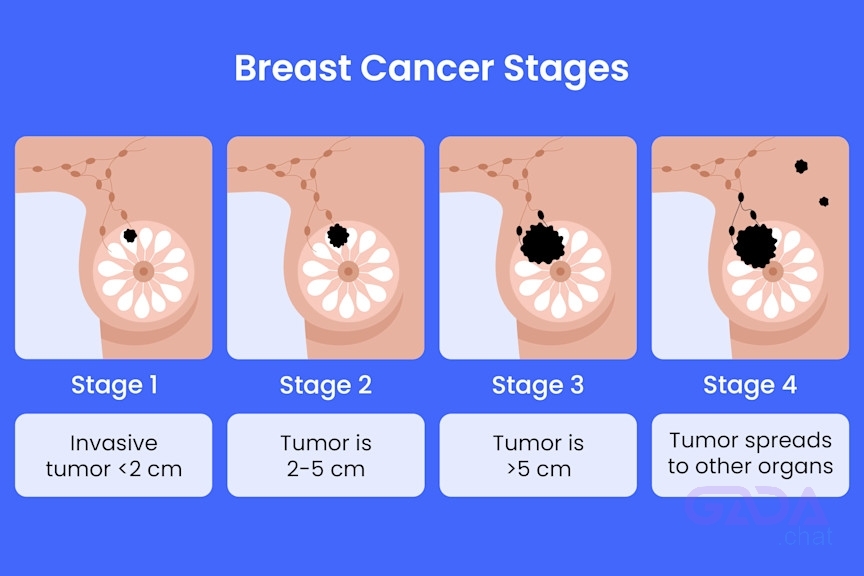
Stages of Breast Cancer:
1. Stage 0: Abnormal cells in breast tissue (non-invasive).
2. Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm) confined to breast tissue.
3. Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer in lymph nodes.
4. Stage III: Large tumor (over 5 cm) or extensive lymph node involvement.
5. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic).
Treatment Options:
1. Surgery: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast-conserving surgery.
2. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
3. Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells.
4. Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone receptors.
5. Targeted therapy: Medications targeting specific cancer cell proteins.
Support and Resources:
1. Breast cancer support groups
2. Oncology teams (doctors, nurses, social workers)
3. Online resources (American Cancer Society, National Breast Cancer Foundation)
4. Local cancer organizations
Let's Take Action:
1. Schedule a mammogram or clinical breast exam.
2. Practice breast self-awareness.
3. Support loved ones affected by breast cancer.
Remember: Early detection saves lives. Let's prioritize breast health and support those affected by breast cancer.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAT – BREAST CANCER (Please Read & Share) Breast Cancer Awareness Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the breast tissue. It's one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates. Key Facts: 1. Risk Factors: Family history, genetics, age, radiation exposure, and hormonal factors. 2. Symptoms: Lump or thickening in the breast, change in breast shape or size, nipple discharge or pain. 3. Screening: Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams. 4. Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. Prevention and Early Detection: 1. Get screened regularly 2. Know your breast health 3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight) 4. Be aware of family history Types of Breast Cancer: 1. Invasive ductal carcinoma: Begins in milk ducts and spreads to surrounding tissue. 2. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Starts in lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads. 3. Triple-negative breast cancer: Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors. 4. HER2-positive breast cancer: Has an overexpression of HER2 protein. Stages of Breast Cancer: 1. Stage 0: Abnormal cells in breast tissue (non-invasive). 2. Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm) confined to breast tissue. 3. Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer in lymph nodes. 4. Stage III: Large tumor (over 5 cm) or extensive lymph node involvement. 5. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic). Treatment Options: 1. Surgery: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast-conserving surgery. 2. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells. 3. Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells. 4. Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone receptors. 5. Targeted therapy: Medications targeting specific cancer cell proteins. Support and Resources: 1. Breast cancer support groups 2. Oncology teams (doctors, nurses, social workers) 3. Online resources (American Cancer Society, National Breast Cancer Foundation) 4. Local cancer organizations Let's Take Action: 1. Schedule a mammogram or clinical breast exam. 2. Practice breast self-awareness. 3. Support loved ones affected by breast cancer. Remember: Early detection saves lives. Let's prioritize breast health and support those affected by breast cancer.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 333 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 173 Visualizações 0 Anterior
-
GEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - ARTHRITIS
ARTHRITIS is a chronic condition that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Here's a more detailed overview:
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a term that encompasses over 100 different conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. It can cause inflammation, pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected joints.
Types of Arthritis:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common type of arthritis, OA is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and joint damage.
3. Psoriatic Arthritis: A type of arthritis that occurs in people with psoriasis, causing joint pain and inflammation.
4. Gout: A type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Causes and Risk Factors:
1. Aging: The risk of developing arthritis increases with age.
2. Genetics: Family history can play a role in the development of certain types of arthritis.
3. Injury or Trauma: Joint injuries can increase the risk of developing arthritis.
4. Obesity: Excess weight can put additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of developing arthritis.
Symptoms:
1. Joint Pain: Pain and stiffness in the affected joints.
2. Swelling and Redness: Inflammation and swelling in the affected joints.
3. Limited Mobility: Reduced range of motion and flexibility in the affected joints.
4. Morning Stiffness: Stiffness and pain in the joints after periods of rest.
Treatment Options:
1. Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
2. Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, weight management, and stress reduction.
3. Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches to improve joint mobility and strength.
4. Surgery: Joint replacement surgery or other surgical procedures to repair or replace damaged joints.
Management Strategies:
1. Stay Active: Regular exercise can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on joints.
3. Use Assistive Devices: Canes, walkers, or other devices can help reduce strain on joints.
4. Get Enough Sleep: Adequate rest can help reduce fatigue and pain.
GEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - ARTHRITIS ARTHRITIS is a chronic condition that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Here's a more detailed overview: What is Arthritis? Arthritis is a term that encompasses over 100 different conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues. It can cause inflammation, pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected joints. Types of Arthritis: 1. Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common type of arthritis, OA is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time. 2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and joint damage. 3. Psoriatic Arthritis: A type of arthritis that occurs in people with psoriasis, causing joint pain and inflammation. 4. Gout: A type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Causes and Risk Factors: 1. Aging: The risk of developing arthritis increases with age. 2. Genetics: Family history can play a role in the development of certain types of arthritis. 3. Injury or Trauma: Joint injuries can increase the risk of developing arthritis. 4. Obesity: Excess weight can put additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of developing arthritis. Symptoms: 1. Joint Pain: Pain and stiffness in the affected joints. 2. Swelling and Redness: Inflammation and swelling in the affected joints. 3. Limited Mobility: Reduced range of motion and flexibility in the affected joints. 4. Morning Stiffness: Stiffness and pain in the joints after periods of rest. Treatment Options: 1. Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). 2. Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, weight management, and stress reduction. 3. Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches to improve joint mobility and strength. 4. Surgery: Joint replacement surgery or other surgical procedures to repair or replace damaged joints. Management Strategies: 1. Stay Active: Regular exercise can help reduce pain and improve mobility. 2. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on joints. 3. Use Assistive Devices: Canes, walkers, or other devices can help reduce strain on joints. 4. Get Enough Sleep: Adequate rest can help reduce fatigue and pain.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 299 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 222 Visualizações 0 Anterior
-
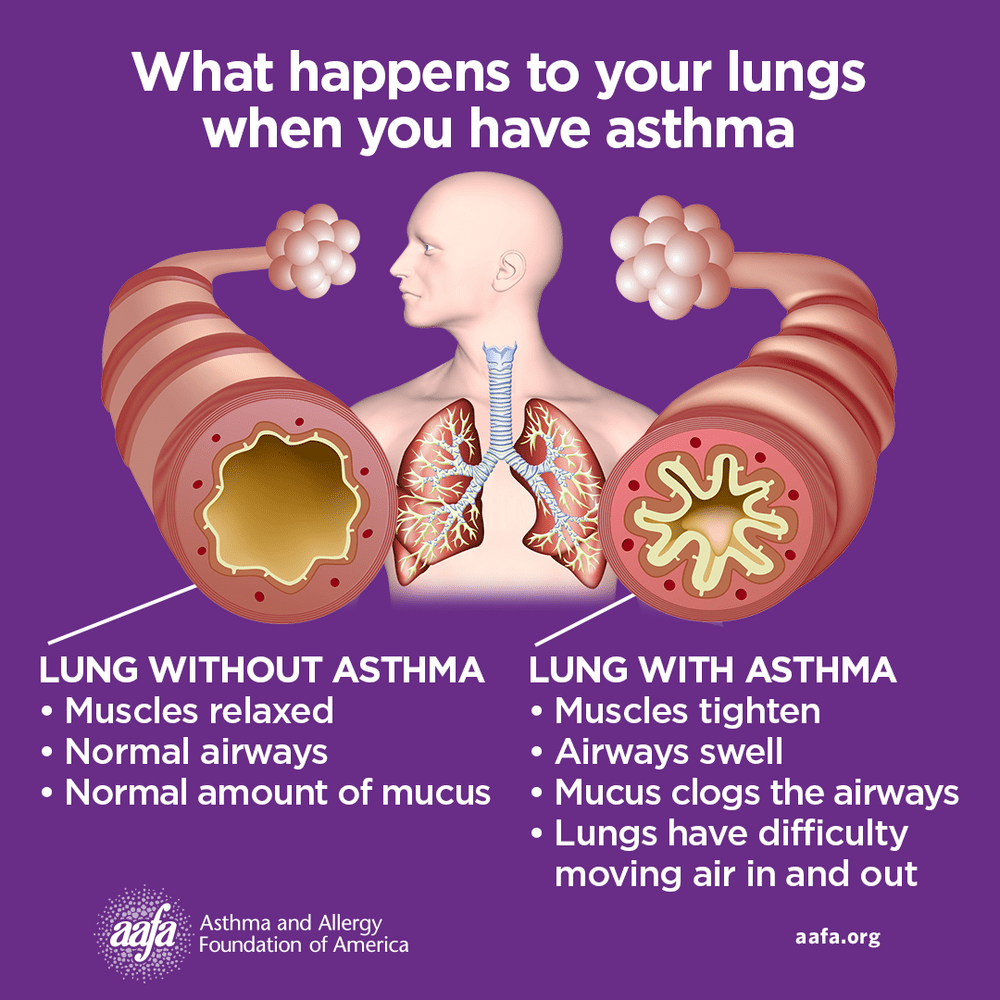
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – ASTHMA (Please Read & Share) part 2
STAGES OR LEVEL OF SEVERITY
Asthma can be classified into different stages or levels of severity. The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) and the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP) provide guidelines for classifying asthma severity.
Asthma Severity Classification
1. Intermittent asthma: Symptoms occur twice a week or less, and nighttime symptoms occur twice a month or less.
2. Mild persistent asthma: Symptoms occur more than twice a week, but not daily, and nighttime symptoms occur more than twice a month.
3. Moderate persistent asthma: Symptoms occur daily, and nighttime symptoms occur more than once a week.
4. Severe persistent asthma: Symptoms occur throughout the day, and nighttime symptoms occur frequently.
Stages of an Asthma Attack
1. Mild: Symptoms are mild, and lung function is slightly impaired.
2. Moderate: Symptoms worsen, and lung function is significantly impaired.
3. Severe: Symptoms are severe, and lung function is severely impaired.
Asthma Control Levels
1. Well-controlled: Symptoms are minimal, and lung function is normal.
2. Not well-controlled: Symptoms occur regularly, and lung function is impaired.
3. Very poorly controlled: Symptoms are severe, and lung function is significantly impaired.
Understanding asthma severity and control levels can help guide treatment decisions and improve asthma management.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – ASTHMA (Please Read & Share) part 2 STAGES OR LEVEL OF SEVERITY Asthma can be classified into different stages or levels of severity. The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) and the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP) provide guidelines for classifying asthma severity. Asthma Severity Classification 1. Intermittent asthma: Symptoms occur twice a week or less, and nighttime symptoms occur twice a month or less. 2. Mild persistent asthma: Symptoms occur more than twice a week, but not daily, and nighttime symptoms occur more than twice a month. 3. Moderate persistent asthma: Symptoms occur daily, and nighttime symptoms occur more than once a week. 4. Severe persistent asthma: Symptoms occur throughout the day, and nighttime symptoms occur frequently. Stages of an Asthma Attack 1. Mild: Symptoms are mild, and lung function is slightly impaired. 2. Moderate: Symptoms worsen, and lung function is significantly impaired. 3. Severe: Symptoms are severe, and lung function is severely impaired. Asthma Control Levels 1. Well-controlled: Symptoms are minimal, and lung function is normal. 2. Not well-controlled: Symptoms occur regularly, and lung function is impaired. 3. Very poorly controlled: Symptoms are severe, and lung function is significantly impaired. Understanding asthma severity and control levels can help guide treatment decisions and improve asthma management.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 177 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – ASTHMA (Please Read & Share) part 1
Understanding Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. It's essential to understand its symptoms, triggers, and management strategies.
Symptoms
1. Wheezing
2. Coughing
3. Shortness of breath
4. Chest tightness
Triggers
1. Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander)
2. Respiratory infections
3. Air pollutants (smoke, pollution)
4. Exercise
5. Stress
Management
1. Medications (inhalers, oral medications)
2. Avoiding triggers
3. Monitoring lung function (peak flow meters)
4. Developing an asthma action plan
Tips for Living with Asthma
1. Stay calm and breathe slowly during attacks
2. Use inhalers as prescribed
3. Monitor peak flow readings
4. Avoid triggers
5. Stay physically active
Importance of Asthma Education
1. Understand asthma and its management
2. Know your triggers and how to avoid them
3. Develop an asthma action plan
4. Stay informed about new treatments and research
Let's dive deeper into asthma management:
Asthma Action Plan
1. Develop a plan: Work with your doctor to create a personalized plan
2. Monitor symptoms: Track your symptoms and lung function
3. Adjust treatment: Adjust medication and treatment based on symptoms
Medications
1. Controller medications: Taken regularly to control symptoms
2. Reliever medications: Taken as needed to relieve acute symptoms
3. Combination therapy: Using multiple medications to control symptoms
Trigger Avoidance
1. Identify triggers: Determine what triggers your asthma symptoms
2. Avoid triggers: Take steps to avoid or minimize exposure to triggers
3. Use protective measures: Use masks, air purifiers, or other protective measures
Lifestyle Changes
1. Stay active: Regular exercise can help improve lung function
2. Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can worsen asthma symptoms
3. Manage stress: Stress-reducing techniques can help manage asthma symptoms
Asthma and Comorbidities
1. Allergies: Common comorbidity with asthma
2. GERD: Can exacerbate asthma symptoms
3. Sleep apnea: Can worsen asthma control
Importance of Regular Check-ups
1. Monitor lung function: Regular check-ups can help monitor lung function
2. Adjust treatment: Treatment plans can be adjusted based on symptoms and lung function
3. Stay informed: Regular check-ups can help you stay informed about your asthma management
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – ASTHMA (Please Read & Share) part 1 Understanding Asthma Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. It's essential to understand its symptoms, triggers, and management strategies. Symptoms 1. Wheezing 2. Coughing 3. Shortness of breath 4. Chest tightness Triggers 1. Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander) 2. Respiratory infections 3. Air pollutants (smoke, pollution) 4. Exercise 5. Stress Management 1. Medications (inhalers, oral medications) 2. Avoiding triggers 3. Monitoring lung function (peak flow meters) 4. Developing an asthma action plan Tips for Living with Asthma 1. Stay calm and breathe slowly during attacks 2. Use inhalers as prescribed 3. Monitor peak flow readings 4. Avoid triggers 5. Stay physically active Importance of Asthma Education 1. Understand asthma and its management 2. Know your triggers and how to avoid them 3. Develop an asthma action plan 4. Stay informed about new treatments and research Let's dive deeper into asthma management: Asthma Action Plan 1. Develop a plan: Work with your doctor to create a personalized plan 2. Monitor symptoms: Track your symptoms and lung function 3. Adjust treatment: Adjust medication and treatment based on symptoms Medications 1. Controller medications: Taken regularly to control symptoms 2. Reliever medications: Taken as needed to relieve acute symptoms 3. Combination therapy: Using multiple medications to control symptoms Trigger Avoidance 1. Identify triggers: Determine what triggers your asthma symptoms 2. Avoid triggers: Take steps to avoid or minimize exposure to triggers 3. Use protective measures: Use masks, air purifiers, or other protective measures Lifestyle Changes 1. Stay active: Regular exercise can help improve lung function 2. Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can worsen asthma symptoms 3. Manage stress: Stress-reducing techniques can help manage asthma symptoms Asthma and Comorbidities 1. Allergies: Common comorbidity with asthma 2. GERD: Can exacerbate asthma symptoms 3. Sleep apnea: Can worsen asthma control Importance of Regular Check-ups 1. Monitor lung function: Regular check-ups can help monitor lung function 2. Adjust treatment: Treatment plans can be adjusted based on symptoms and lung function 3. Stay informed: Regular check-ups can help you stay informed about your asthma management0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 309 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
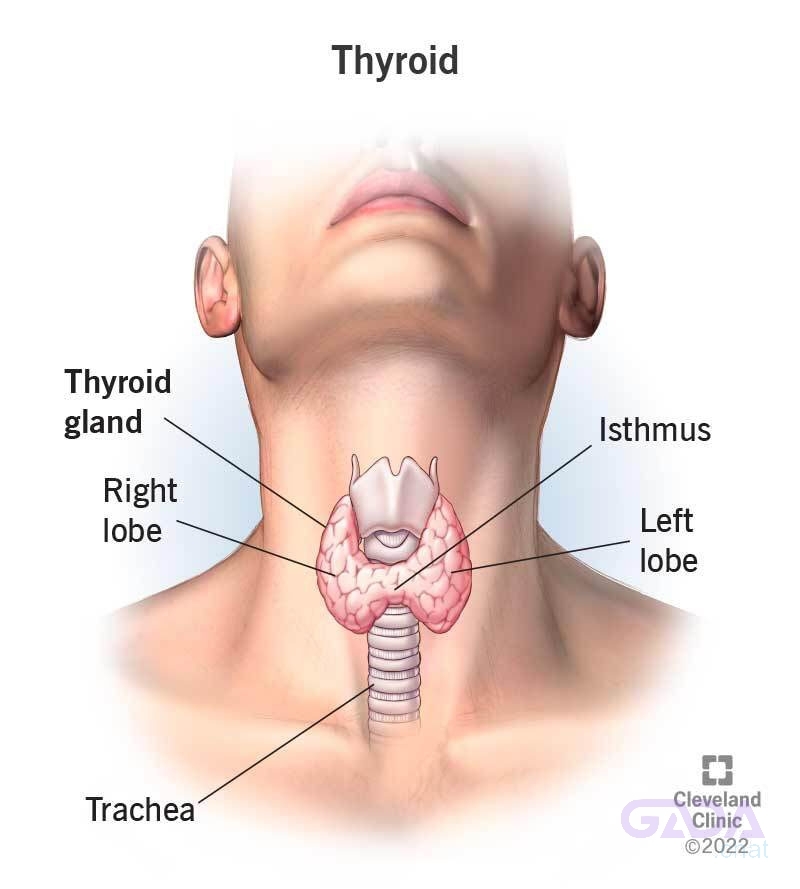
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share)
Part 2
If the thyroid gland is removed, either partially or entirely, it can have significant effects on the body.
Effects of Thyroid Removal
1. Hormone regulation: The body will no longer be able to produce thyroid hormones on its own.
2. Medication dependency: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate your metabolism.
3. Metabolic changes: Your metabolism may slow down, potentially leading to weight gain.
4. Energy levels: You may experience fatigue, weakness, or lethargy.
Types of Thyroid Removal
1. Partial thyroidectomy: Removing part of the thyroid gland.
2. Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire thyroid gland.
Post-Surgery Care
1. Medication management: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication as prescribed.
2. Regular check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
3. Lifestyle adjustments: You may need to make dietary changes or adjust your exercise routine.
Potential Complications
1. Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, which can be managed with medication.
2. Voice changes: Temporary or permanent changes to your voice.
3. Calcium levels: Potential impact on calcium levels in the body.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper medication management and care, many people can lead normal lives after thyroid removal surgery
THYROID CANCER is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating growth and metabolism.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
1. Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common type, often slow-growing.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, can spread to bones and lungs.
3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Rare, often linked to genetic mutations.
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Rare, aggressive, and fast-growing.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetic mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic mutations.
2. Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood.
3. Family history: Family history of thyroid cancer.
Symptoms
1. Neck lump: A lump or swelling in the neck.
2. Voice changes: Hoarseness or voice changes.
3. Swallowing difficulties: Difficulty swallowing.
4. Neck pain: Pain in the neck.
Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to diagnose cancer.
2. Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
3. Radioactive iodine therapy: Treatment to destroy remaining cancer cells.
4. Thyroid hormone replacement: Medication to replace thyroid hormones.
Prognosis
Thyroid cancer has a high cure rate, especially if detected early. The prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer.HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share) Part 2 If the thyroid gland is removed, either partially or entirely, it can have significant effects on the body. Effects of Thyroid Removal 1. Hormone regulation: The body will no longer be able to produce thyroid hormones on its own. 2. Medication dependency: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate your metabolism. 3. Metabolic changes: Your metabolism may slow down, potentially leading to weight gain. 4. Energy levels: You may experience fatigue, weakness, or lethargy. Types of Thyroid Removal 1. Partial thyroidectomy: Removing part of the thyroid gland. 2. Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire thyroid gland. Post-Surgery Care 1. Medication management: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication as prescribed. 2. Regular check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels. 3. Lifestyle adjustments: You may need to make dietary changes or adjust your exercise routine. Potential Complications 1. Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, which can be managed with medication. 2. Voice changes: Temporary or permanent changes to your voice. 3. Calcium levels: Potential impact on calcium levels in the body. Long-Term Outlook With proper medication management and care, many people can lead normal lives after thyroid removal surgery THYROID CANCER is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating growth and metabolism. Types of Thyroid Cancer 1. Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common type, often slow-growing. 2. Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, can spread to bones and lungs. 3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Rare, often linked to genetic mutations. 4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Rare, aggressive, and fast-growing. Causes and Risk Factors 1. Genetic mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic mutations. 2. Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood. 3. Family history: Family history of thyroid cancer. Symptoms 1. Neck lump: A lump or swelling in the neck. 2. Voice changes: Hoarseness or voice changes. 3. Swallowing difficulties: Difficulty swallowing. 4. Neck pain: Pain in the neck. Diagnosis and Treatment 1. Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to diagnose cancer. 2. Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). 3. Radioactive iodine therapy: Treatment to destroy remaining cancer cells. 4. Thyroid hormone replacement: Medication to replace thyroid hormones. Prognosis Thyroid cancer has a high cure rate, especially if detected early. The prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 228 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share)
Part 1 of 2
The thyroid gland is a vital part of the human body!
What is the Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions.
Functions of the Thyroid Gland
1. Metabolism regulation: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth.
2. Hormone production: The thyroid gland produces two main hormones: Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4).
3. Growth and development: Thyroid hormones are essential for growth and development, particularly in children and adolescents.
Importance of the Thyroid Gland
1. Energy levels: Thyroid hormones help regulate energy levels and metabolism.
2. Weight management: Thyroid hormones play a role in weight management and metabolism.
3. Mood regulation: Thyroid hormones can influence mood and emotional well-being.
Common Thyroid Disorders
1. Hypothyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones.
2. Hyperthyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland produces too many hormones.
3. Thyroid nodules: Abnormal growths on the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
1. Fatigue: Feeling tired or sluggish.
2. Weight changes: Unexplained weight gain or loss.
3. Mood changes: Mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Blood tests: Blood tests can help diagnose thyroid disorders.
2. Medications: Medications can help manage thyroid hormone levels.
3. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share) Part 1 of 2 The thyroid gland is a vital part of the human body! What is the Thyroid Gland? The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. Functions of the Thyroid Gland 1. Metabolism regulation: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. 2. Hormone production: The thyroid gland produces two main hormones: Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4). 3. Growth and development: Thyroid hormones are essential for growth and development, particularly in children and adolescents. Importance of the Thyroid Gland 1. Energy levels: Thyroid hormones help regulate energy levels and metabolism. 2. Weight management: Thyroid hormones play a role in weight management and metabolism. 3. Mood regulation: Thyroid hormones can influence mood and emotional well-being. Common Thyroid Disorders 1. Hypothyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones. 2. Hyperthyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland produces too many hormones. 3. Thyroid nodules: Abnormal growths on the thyroid gland. Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders 1. Fatigue: Feeling tired or sluggish. 2. Weight changes: Unexplained weight gain or loss. 3. Mood changes: Mood swings, anxiety, or depression. Diagnosis and Treatment 1. Blood tests: Blood tests can help diagnose thyroid disorders. 2. Medications: Medications can help manage thyroid hormone levels. 3. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 220 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
THE ROLE OF WATER IN HUMAN – part 2
Here are some additional aspects of water:
Water's Role in Human Health
1. Hydration: Water helps regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and remove waste.
2. Digestion: Water aids in digestion and prevents constipation.
3. Skin Health: Water helps maintain skin elasticity and hydration.
Industrial Uses of Water
1. Manufacturing: Water is used in production processes, cleaning, and cooling.
2. Energy Production: Water is used in power plants for cooling and steam generation.
3. Mining: Water is used in mining operations for extraction and processing.
Environmental Impact
1. Water Pollution: Human activities can pollute water sources, harming ecosystems and wildlife.
2. Climate Change: Climate change affects water availability, quality, and distribution.
3. Water Conservation: Conserving water helps protect ecosystems and ensure sustainable use.
Interesting Water Facts
1. Water's High Specific Heat Capacity: Water can absorb and release large amounts of heat energy without a significant change in temperature.
2. Water's Role in Weather: Water plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns, including precipitation and storms.
3. Water's Importance in Agriculture: Water is essential for crop growth, and efficient irrigation systems can help conserve water.
Water Technology
1. Water Treatment: Advanced water treatment technologies can remove contaminants and improve water quality.
2. Desalination: Desalination plants can provide freshwater for drinking and irrigation in coastal areas.
3. Water Recycling: Water recycling can help conserve water resources and reduce wastewater.
Global Water Challenges
1. Water Scarcity: Many regions face water scarcity, affecting human consumption, agriculture, and ecosystems.
2. Water Quality: Ensuring access to clean and safe water is a significant challenge worldwide.
3. Water Management: Effective water management strategies are crucial for sustainable water use and conservation.
Let's dive deeper into Water Scarcity.
Causes of Water Scarcity
1. Climate Change: Changes in precipitation patterns and increased evaporation due to rising temperatures.
2. Population Growth: Increased demand for water due to growing populations.
3. Over-Extraction: Excessive withdrawal of groundwater, leading to depletion of aquifers.
4. Water Pollution: Contamination of water sources, making them unusable.
Impacts of Water Scarcity
1. Food Security: Water scarcity can lead to crop failures, reduced yields, and food insecurity.
2. Human Health: Lack of access to clean water can lead to waterborne diseases, dehydration, and other health issues.
3. Economic Consequences: Water scarcity can impact industries, agriculture, and tourism, leading to economic losses.
4. Social Stability: Water scarcity can lead to conflicts, migration, and social unrest.
Solutions to Water Scarcity
1. Water Conservation: Implementing efficient irrigation systems, fixing leaks, and promoting water-saving practices.
2. Water Recycling: Treating and reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes.
3. Desalination: Using technologies to remove salt and minerals from seawater or brackish water.
4. Sustainable Water Management: Implementing policies, practices, and technologies to manage water resources effectively.
What Can You Do?
1. Conserve Water: Take shorter showers, fix leaks, and use water-efficient appliances.
2. Support Water-Efficient Technologies: Invest in technologies that promote water conservation.
3. Raise Awareness: Educate others about the importance of water conservation.
THE ROLE OF WATER IN HUMAN – part 2 Here are some additional aspects of water: Water's Role in Human Health 1. Hydration: Water helps regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and remove waste. 2. Digestion: Water aids in digestion and prevents constipation. 3. Skin Health: Water helps maintain skin elasticity and hydration. Industrial Uses of Water 1. Manufacturing: Water is used in production processes, cleaning, and cooling. 2. Energy Production: Water is used in power plants for cooling and steam generation. 3. Mining: Water is used in mining operations for extraction and processing. Environmental Impact 1. Water Pollution: Human activities can pollute water sources, harming ecosystems and wildlife. 2. Climate Change: Climate change affects water availability, quality, and distribution. 3. Water Conservation: Conserving water helps protect ecosystems and ensure sustainable use. Interesting Water Facts 1. Water's High Specific Heat Capacity: Water can absorb and release large amounts of heat energy without a significant change in temperature. 2. Water's Role in Weather: Water plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns, including precipitation and storms. 3. Water's Importance in Agriculture: Water is essential for crop growth, and efficient irrigation systems can help conserve water. Water Technology 1. Water Treatment: Advanced water treatment technologies can remove contaminants and improve water quality. 2. Desalination: Desalination plants can provide freshwater for drinking and irrigation in coastal areas. 3. Water Recycling: Water recycling can help conserve water resources and reduce wastewater. Global Water Challenges 1. Water Scarcity: Many regions face water scarcity, affecting human consumption, agriculture, and ecosystems. 2. Water Quality: Ensuring access to clean and safe water is a significant challenge worldwide. 3. Water Management: Effective water management strategies are crucial for sustainable water use and conservation. Let's dive deeper into Water Scarcity. Causes of Water Scarcity 1. Climate Change: Changes in precipitation patterns and increased evaporation due to rising temperatures. 2. Population Growth: Increased demand for water due to growing populations. 3. Over-Extraction: Excessive withdrawal of groundwater, leading to depletion of aquifers. 4. Water Pollution: Contamination of water sources, making them unusable. Impacts of Water Scarcity 1. Food Security: Water scarcity can lead to crop failures, reduced yields, and food insecurity. 2. Human Health: Lack of access to clean water can lead to waterborne diseases, dehydration, and other health issues. 3. Economic Consequences: Water scarcity can impact industries, agriculture, and tourism, leading to economic losses. 4. Social Stability: Water scarcity can lead to conflicts, migration, and social unrest. Solutions to Water Scarcity 1. Water Conservation: Implementing efficient irrigation systems, fixing leaks, and promoting water-saving practices. 2. Water Recycling: Treating and reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes. 3. Desalination: Using technologies to remove salt and minerals from seawater or brackish water. 4. Sustainable Water Management: Implementing policies, practices, and technologies to manage water resources effectively. What Can You Do? 1. Conserve Water: Take shorter showers, fix leaks, and use water-efficient appliances. 2. Support Water-Efficient Technologies: Invest in technologies that promote water conservation. 3. Raise Awareness: Educate others about the importance of water conservation.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 335 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – WATER (H2O) – Part 1 of 2
Water is a fascinating substance that plays a crucial role in our lives and the planet. Here's a rundown:
Properties of Water
1. Chemical Composition: Water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O).
2. States: Water can exist in three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor).
3. Viscosity: Water has a relatively low viscosity, making it flow easily.
4. Surface Tension: Water has a high surface tension, allowing it to hold its shape against gravity.
Importance of Water
1. Life Support: Water is essential for human life, supporting bodily functions, and regulating temperature.
2. Ecosystems: Water is vital for plant and animal survival, shaping landscapes, and influencing climate.
3. Agriculture: Water is crucial for crop growth, irrigation, and food production.
4. Industry: Water is used in various industries, such as manufacturing, energy production, and mining.
Water Cycle
1. Evaporation: Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and rivers into the atmosphere.
2. Condensation: Water vapor condenses into clouds.
3. Precipitation: Water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Water Conservation
1. Scarcity: Water scarcity affects many regions, making conservation essential.
2. Efficient Use: Using water-efficient appliances, fixing leaks, and adopting sustainable practices can help conserve water.
3. Water Management: Effective water management strategies, such as water recycling and harvesting, can also help.
Water Quality
1. Pollution: Water pollution from human activities, such as industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage, can harm ecosystems and human health.
2. Treatment: Water treatment processes, such as filtration and disinfection, can improve water quality.
Fun Facts
1. Water Coverage: About 71% of the Earth's surface is water.
2. Freshwater: Only about 2.5% of the Earth's water is freshwater.
3. Water in the Body: Humans are composed of approximately 60% water.
That's just a glimpse into the amazing world of water! – To be continue
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – WATER (H2O) – Part 1 of 2 Water is a fascinating substance that plays a crucial role in our lives and the planet. Here's a rundown: Properties of Water 1. Chemical Composition: Water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O). 2. States: Water can exist in three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor). 3. Viscosity: Water has a relatively low viscosity, making it flow easily. 4. Surface Tension: Water has a high surface tension, allowing it to hold its shape against gravity. Importance of Water 1. Life Support: Water is essential for human life, supporting bodily functions, and regulating temperature. 2. Ecosystems: Water is vital for plant and animal survival, shaping landscapes, and influencing climate. 3. Agriculture: Water is crucial for crop growth, irrigation, and food production. 4. Industry: Water is used in various industries, such as manufacturing, energy production, and mining. Water Cycle 1. Evaporation: Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and rivers into the atmosphere. 2. Condensation: Water vapor condenses into clouds. 3. Precipitation: Water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Water Conservation 1. Scarcity: Water scarcity affects many regions, making conservation essential. 2. Efficient Use: Using water-efficient appliances, fixing leaks, and adopting sustainable practices can help conserve water. 3. Water Management: Effective water management strategies, such as water recycling and harvesting, can also help. Water Quality 1. Pollution: Water pollution from human activities, such as industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage, can harm ecosystems and human health. 2. Treatment: Water treatment processes, such as filtration and disinfection, can improve water quality. Fun Facts 1. Water Coverage: About 71% of the Earth's surface is water. 2. Freshwater: Only about 2.5% of the Earth's water is freshwater. 3. Water in the Body: Humans are composed of approximately 60% water. That's just a glimpse into the amazing world of water! – To be continue0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 257 Visualizações 0 Anterior1
-
HEALTHCARE FOR TODAY - (Please Read and Comments)
THE HUMAN EYE is a complex and fascinating organ that enables us to perceive and interpret the world around us. Here's a comprehensive overview:
STRUCTURE OF THE EYE
1. Cornea: The transparent outer layer that helps focus light.
2. Iris: The colored part that controls the amount of light entering the eye.
3. Pupil: The opening in the center of the iris that regulates light entry.
4. Lens: A flexible structure that changes shape to focus light on the retina.
5. Retina: The innermost layer containing light-sensitive cells (photoreceptors) that convert light into electrical signals.
6. Macula: A specialized area at the center of the retina responsible for central vision and fine detail.
7. Optic Nerve: The nerve that transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
HOW THE EYE WORKS
1. Light Entry: Light enters the eye through the cornea and pupil.
2. Focusing: The lens changes shape to focus light on the retina.
3. Signal Transmission: Photoreceptors in the retina convert light into electrical signals.
4. Signal Processing: The optic nerve transmits electrical signals to the brain.
5. Image Formation: The brain interprets electrical signals as visual images.
COMMON EYE CONDITIONS
MYOPIA (NEARSIGHTEDNESS)
1. Definition: Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly due to elongated eyeball or curved cornea.
2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, squinting, headaches.
3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery.
HYPEROPIA (FARSIGHTEDNESS)
1. Definition: Difficulty seeing close objects clearly due to shortened eyeball or flat cornea.
2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, eye strain, headaches.
3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery.
ASTIGMATISM
1. Definition: Blurred vision due to irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, eye strain, headaches.
3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery.
CATARACTS
1. Definition: Clouding of the lens that affects vision.
2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, glare, double vision.
3. Treatment: Surgery to remove cloudy lens and replace with artificial lens.
GLAUCOMA
1. Definition: Increased pressure in the eye that can damage the optic nerve.
2. Symptoms: Often asymptomatic in early stages, gradual vision loss.
3. Treatment: Medications, laser treatment, surgery.
AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION (AMD)
1. Definition: A leading cause of vision loss in older adults, affecting central vision.
2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, distorted vision, blind spots.
3. Treatment: Vitamins and minerals, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections.
OTHER COMMON EYE CONDITIONS
1. Dry Eye Syndrome: Insufficient tear production or poor tear quality.
2. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva.
3. Presbyopia: Age-related decline in near vision.
EYE CARE AND PROTECTION
1. Regular Eye Exams: Schedule regular eye exams to detect potential issues early.
2. Protective Eyewear: Wear safety glasses or goggles when engaging in activities that pose a risk to your eyes.
3. UV Protection: Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays.
4. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support eye health.
INTERESTING FACTS
1. Unique Iris Patterns: Each person's iris pattern is unique, like a fingerprint.
2. Blinking: We blink around 12-15 times per minute to keep our eyes moist and clean.
3. Color Perception: The human eye can distinguish between millions of colors.
HEALTHCARE FOR TODAY - (Please Read and Comments) THE HUMAN EYE is a complex and fascinating organ that enables us to perceive and interpret the world around us. Here's a comprehensive overview: STRUCTURE OF THE EYE 1. Cornea: The transparent outer layer that helps focus light. 2. Iris: The colored part that controls the amount of light entering the eye. 3. Pupil: The opening in the center of the iris that regulates light entry. 4. Lens: A flexible structure that changes shape to focus light on the retina. 5. Retina: The innermost layer containing light-sensitive cells (photoreceptors) that convert light into electrical signals. 6. Macula: A specialized area at the center of the retina responsible for central vision and fine detail. 7. Optic Nerve: The nerve that transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain. HOW THE EYE WORKS 1. Light Entry: Light enters the eye through the cornea and pupil. 2. Focusing: The lens changes shape to focus light on the retina. 3. Signal Transmission: Photoreceptors in the retina convert light into electrical signals. 4. Signal Processing: The optic nerve transmits electrical signals to the brain. 5. Image Formation: The brain interprets electrical signals as visual images. COMMON EYE CONDITIONS MYOPIA (NEARSIGHTEDNESS) 1. Definition: Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly due to elongated eyeball or curved cornea. 2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, squinting, headaches. 3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery. HYPEROPIA (FARSIGHTEDNESS) 1. Definition: Difficulty seeing close objects clearly due to shortened eyeball or flat cornea. 2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, eye strain, headaches. 3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery. ASTIGMATISM 1. Definition: Blurred vision due to irregularly shaped cornea or lens. 2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, eye strain, headaches. 3. Treatment: Glasses, contact lenses, refractive surgery. CATARACTS 1. Definition: Clouding of the lens that affects vision. 2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, glare, double vision. 3. Treatment: Surgery to remove cloudy lens and replace with artificial lens. GLAUCOMA 1. Definition: Increased pressure in the eye that can damage the optic nerve. 2. Symptoms: Often asymptomatic in early stages, gradual vision loss. 3. Treatment: Medications, laser treatment, surgery. AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION (AMD) 1. Definition: A leading cause of vision loss in older adults, affecting central vision. 2. Symptoms: Blurred vision, distorted vision, blind spots. 3. Treatment: Vitamins and minerals, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections. OTHER COMMON EYE CONDITIONS 1. Dry Eye Syndrome: Insufficient tear production or poor tear quality. 2. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva. 3. Presbyopia: Age-related decline in near vision. EYE CARE AND PROTECTION 1. Regular Eye Exams: Schedule regular eye exams to detect potential issues early. 2. Protective Eyewear: Wear safety glasses or goggles when engaging in activities that pose a risk to your eyes. 3. UV Protection: Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays. 4. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support eye health. INTERESTING FACTS 1. Unique Iris Patterns: Each person's iris pattern is unique, like a fingerprint. 2. Blinking: We blink around 12-15 times per minute to keep our eyes moist and clean. 3. Color Perception: The human eye can distinguish between millions of colors.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 382 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY
- REFLEXOLOGY (PLEASE READ AND COMMENT)
Reflexology is a holistic practice that involves applying pressure to specific points on the feet, hands, or ears to promote relaxation, balance, and wellbeing. This include:
1. *Toes*: Associated with the head and brain, gentle massage or pressure on the toes might promote relaxation.
2. *Solar Plexus Point*: Located on the arch of the foot, this point is believed to help reduce stress and anxiety.
3. *Pituitary Gland Point*: Some reflexologists suggest that this point, often located on the big toe, may help regulate hormonal balance and promote overall wellbeing.
Keep in mind that while reflexology can be relaxing, its effectiveness for specific health benefits varies, and more research is needed.
Benefits of Reflexology
1. *Stress Reduction*: Reflexology can help calm the mind and body.
2. *Improved Sleep*: Regular sessions may enhance sleep quality.
3. *Pain Relief*: Reflexology might help alleviate pain, including headaches and migraines.
4. *Increased Circulation*: Improved blood flow can benefit overall health.
Relaxation Techniques
1. *Deep Breathing*: Focus on slow, deliberate breaths.
2. *Progressive Muscle Relaxation*: Tense and release muscles systematically.
3. *Mindfulness Meditation*: Focus on the present moment.
4. *Yoga*: Combine physical postures, breathing, and meditation.
Additional Tips
1. *Find a Qualified Practitioner*: Look for certified reflexologists or therapists.
2. *Communicate Your Needs*: Share your goals and concerns with your practitioner.
3. *Combine with Other Therapies*: Reflexology can complement traditional treatments.
Thanks !!!
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - REFLEXOLOGY (PLEASE READ AND COMMENT) Reflexology is a holistic practice that involves applying pressure to specific points on the feet, hands, or ears to promote relaxation, balance, and wellbeing. This include: 1. *Toes*: Associated with the head and brain, gentle massage or pressure on the toes might promote relaxation. 2. *Solar Plexus Point*: Located on the arch of the foot, this point is believed to help reduce stress and anxiety. 3. *Pituitary Gland Point*: Some reflexologists suggest that this point, often located on the big toe, may help regulate hormonal balance and promote overall wellbeing. Keep in mind that while reflexology can be relaxing, its effectiveness for specific health benefits varies, and more research is needed. Benefits of Reflexology 1. *Stress Reduction*: Reflexology can help calm the mind and body. 2. *Improved Sleep*: Regular sessions may enhance sleep quality. 3. *Pain Relief*: Reflexology might help alleviate pain, including headaches and migraines. 4. *Increased Circulation*: Improved blood flow can benefit overall health. Relaxation Techniques 1. *Deep Breathing*: Focus on slow, deliberate breaths. 2. *Progressive Muscle Relaxation*: Tense and release muscles systematically. 3. *Mindfulness Meditation*: Focus on the present moment. 4. *Yoga*: Combine physical postures, breathing, and meditation. Additional Tips 1. *Find a Qualified Practitioner*: Look for certified reflexologists or therapists. 2. *Communicate Your Needs*: Share your goals and concerns with your practitioner. 3. *Combine with Other Therapies*: Reflexology can complement traditional treatments. Thanks !!!0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 387 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
Influence of Culture on Health
Culture and health are intricately linked, influencing one another in complex ways.
What is Culture?
Culture refers to the shared patterns of ideas, customs, and behaviors of a particular group or society. It's dynamic, evolving, and learned through generations. Culture encompasses various aspects, including:
• Ethnicity: Shared heritage, traditions, and values
• Language: Verbal and non-verbal communication
• Religion and Spiritual Beliefs: Faith, rituals, and practices
• Socio-economic Class: Economic status, education, and occupation
• Age: Generational differences and experiences
• Sexual Orientation: Identity, community, and relationships
• Geographic Origin: Regional customs, climate, and environment
• Group History: Collective experiences, memories, and narratives
• Education: Formal and informal learning, knowledge, and skills
• Upbringing: Family, community, and socialization
How Culture Influences Health
Culture affects health in numerous ways¹:
• Perceptions of Health and Illness: Cultural beliefs shape understanding of health, disease, and wellness
• Health-seeking Behavior: Cultural factors influence when and how patients seek medical help
• Treatment Adherence: Cultural values impact patients' willingness to follow treatment plans
• Communication: Cultural differences affect patient-provider interactions and understanding
• Health Outcomes: Cultural factors contribute to health disparities and inequities
Influence of Culture on Health Culture and health are intricately linked, influencing one another in complex ways. What is Culture? Culture refers to the shared patterns of ideas, customs, and behaviors of a particular group or society. It's dynamic, evolving, and learned through generations. Culture encompasses various aspects, including: • Ethnicity: Shared heritage, traditions, and values • Language: Verbal and non-verbal communication • Religion and Spiritual Beliefs: Faith, rituals, and practices • Socio-economic Class: Economic status, education, and occupation • Age: Generational differences and experiences • Sexual Orientation: Identity, community, and relationships • Geographic Origin: Regional customs, climate, and environment • Group History: Collective experiences, memories, and narratives • Education: Formal and informal learning, knowledge, and skills • Upbringing: Family, community, and socialization How Culture Influences Health Culture affects health in numerous ways¹: • Perceptions of Health and Illness: Cultural beliefs shape understanding of health, disease, and wellness • Health-seeking Behavior: Cultural factors influence when and how patients seek medical help • Treatment Adherence: Cultural values impact patients' willingness to follow treatment plans • Communication: Cultural differences affect patient-provider interactions and understanding • Health Outcomes: Cultural factors contribute to health disparities and inequities0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 511 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, also known as HYPERTENSION, is when the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high. It's like having a strong flow of water through a hose, which can put extra strain on the hose's walls.
What Happens
1. Blood vessels: Your blood vessels can get damaged, making it harder for blood to flow.
2. Heart: Your heart has to work harder to pump blood, which can lead to heart problems.
3. Other organs: High blood pressure can also affect your kidneys, eyes, and brain.
Managing It
1. Healthy habits: Eating well, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help.
2. Medications: If needed, medications can help lower blood pressure.
3. Regular checks: Monitoring your blood pressure regularly can help you stay on top of it.
BLOOD PRESSURE CALCULATION
Blood Pressure category Systolic mm Hg (Upper No.) Diastolic mm Hg (Lower No.)
NORMAL LESS THAN 120 LESS THAN 80
ELEVATED 120 – 129 LESS THAN 80
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
(HYPERTENSION) STAGE 1 130 – 139 80 - 89
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
(HYPERTENSION) STAGE 2 140 OR HIGHER 90 OR HIGHER
HYPERTENSIVE HIGHER THEN 180 HIGHER THAN 120
CRISIS (Consult your doctor)
Dietary Changes
1. Reduce sodium: Limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day.
2. Increase potassium: Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes.
3. Focus on whole foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy.
Exercise and Physical Activity
1. Regular exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days.
2. Aerobic exercise: Engage in activities like walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming.
3. Strength training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle.
Stress Management
1. Relaxation techniques: Practice deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
2. Time management: Prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and take breaks.
3. Social support: Connect with friends, family, or support groups.
Monitoring and Tracking
1. Regular blood pressure checks: Track your progress and adjust treatment as needed.
2. Home monitoring: Consider using a home blood pressure monitor to track your readings.
3. Medication adherence: Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
1. Regular check-ups: Schedule regular appointments to monitor your blood pressure.
2. Open communication: Discuss any concerns, questions, or challenges with your healthcare provider.
3. Collaborative treatment planning: Work together to develop a personalized treatment plan.
By making these lifestyle changes and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage high blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE, also known as HYPERTENSION, is when the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high. It's like having a strong flow of water through a hose, which can put extra strain on the hose's walls. What Happens 1. Blood vessels: Your blood vessels can get damaged, making it harder for blood to flow. 2. Heart: Your heart has to work harder to pump blood, which can lead to heart problems. 3. Other organs: High blood pressure can also affect your kidneys, eyes, and brain. Managing It 1. Healthy habits: Eating well, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help. 2. Medications: If needed, medications can help lower blood pressure. 3. Regular checks: Monitoring your blood pressure regularly can help you stay on top of it. BLOOD PRESSURE CALCULATION Blood Pressure category Systolic mm Hg (Upper No.) Diastolic mm Hg (Lower No.) NORMAL LESS THAN 120 LESS THAN 80 ELEVATED 120 – 129 LESS THAN 80 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE (HYPERTENSION) STAGE 1 130 – 139 80 - 89 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE (HYPERTENSION) STAGE 2 140 OR HIGHER 90 OR HIGHER HYPERTENSIVE HIGHER THEN 180 HIGHER THAN 120 CRISIS (Consult your doctor) Dietary Changes 1. Reduce sodium: Limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day. 2. Increase potassium: Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes. 3. Focus on whole foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. Exercise and Physical Activity 1. Regular exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days. 2. Aerobic exercise: Engage in activities like walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. 3. Strength training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle. Stress Management 1. Relaxation techniques: Practice deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. 2. Time management: Prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and take breaks. 3. Social support: Connect with friends, family, or support groups. Monitoring and Tracking 1. Regular blood pressure checks: Track your progress and adjust treatment as needed. 2. Home monitoring: Consider using a home blood pressure monitor to track your readings. 3. Medication adherence: Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Working with Your Healthcare Provider 1. Regular check-ups: Schedule regular appointments to monitor your blood pressure. 2. Open communication: Discuss any concerns, questions, or challenges with your healthcare provider. 3. Collaborative treatment planning: Work together to develop a personalized treatment plan. By making these lifestyle changes and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage high blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 436 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
DEPRRSSION AND DISORDERS -part 2 continue
Let's dive deeper into depression and mood disorders:
Causes and Risk Factors
1. *Genetics*: Family history can play a role in the development of mood disorders.
2. *Brain chemistry*: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can contribute to depression.
3. *Life events*: Traumatic experiences, stress, and significant life changes can trigger depression.
4. *Medical conditions*: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or chronic pain, can increase the risk of depression.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
1. *Persistent feelings*: Sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness that lasts for weeks or months.
2. *Loss of interest*: Decreased interest in activities, hobbies, or social interactions.
3. *Physical symptoms*: Changes in appetite, sleep patterns, or energy levels.
4. *Cognitive symptoms*: Difficulty concentrating, making decisions, or remembering things.
Treatment Approaches
1. *Medications*: Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics can help manage symptoms.
2. *Therapy*: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), or psychodynamic therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies.
3. *Lifestyle changes*: Regular exercise, healthy diet, social support, and stress management can also be beneficial.
Support and Resources
1. *Mental health professionals*: Psychiatrists, therapists, or counselors can provide diagnosis, treatment, and support.
2. *Support groups*: Online or in-person groups can provide a sense of community and connection.
3. *Hotlines and helplines*: Confidential support and resources are available 24/7.
If you're struggling with depression or mood disorders, remember that you're not alone, and there is help available.DEPRRSSION AND DISORDERS -part 2 continue Let's dive deeper into depression and mood disorders: Causes and Risk Factors 1. *Genetics*: Family history can play a role in the development of mood disorders. 2. *Brain chemistry*: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can contribute to depression. 3. *Life events*: Traumatic experiences, stress, and significant life changes can trigger depression. 4. *Medical conditions*: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or chronic pain, can increase the risk of depression. Symptoms and Diagnosis 1. *Persistent feelings*: Sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness that lasts for weeks or months. 2. *Loss of interest*: Decreased interest in activities, hobbies, or social interactions. 3. *Physical symptoms*: Changes in appetite, sleep patterns, or energy levels. 4. *Cognitive symptoms*: Difficulty concentrating, making decisions, or remembering things. Treatment Approaches 1. *Medications*: Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics can help manage symptoms. 2. *Therapy*: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), or psychodynamic therapy can help individuals develop coping strategies. 3. *Lifestyle changes*: Regular exercise, healthy diet, social support, and stress management can also be beneficial. Support and Resources 1. *Mental health professionals*: Psychiatrists, therapists, or counselors can provide diagnosis, treatment, and support. 2. *Support groups*: Online or in-person groups can provide a sense of community and connection. 3. *Hotlines and helplines*: Confidential support and resources are available 24/7. If you're struggling with depression or mood disorders, remember that you're not alone, and there is help available.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 341 Visualizações 0 Anterior1
-
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - part 1
DEPRESSION AND MOOD DISORDERS
Depression and mood disorders are mental health conditions that affect a person's emotional state and overall well-being. They can impact daily life, relationships, and physical health.
Types of Mood Disorders
1. *Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)*: Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
2. *Bipolar Disorder*: Mood swings between depression and mania or hypomania.
3. *Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)*: Depression that occurs during specific seasons, often winter.
Symptoms
1. *Emotional changes*: Feelings of sadness, emptiness, or irritability.
2. *Changes in appetite or sleep*: Increased or decreased appetite, insomnia, or excessive sleep.
3. *Loss of interest*: Decreased interest in activities, hobbies, or social interactions.
4. *Physical symptoms*: Fatigue, headaches, or digestive problems.
Treatment Options
1. *Therapy*: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), or psychodynamic therapy.
2. *Medication*: Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics.
3. *Lifestyle changes*: Regular exercise, healthy diet, social support, and stress management.
To be continue
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - part 1 DEPRESSION AND MOOD DISORDERS Depression and mood disorders are mental health conditions that affect a person's emotional state and overall well-being. They can impact daily life, relationships, and physical health. Types of Mood Disorders 1. *Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)*: Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. 2. *Bipolar Disorder*: Mood swings between depression and mania or hypomania. 3. *Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)*: Depression that occurs during specific seasons, often winter. Symptoms 1. *Emotional changes*: Feelings of sadness, emptiness, or irritability. 2. *Changes in appetite or sleep*: Increased or decreased appetite, insomnia, or excessive sleep. 3. *Loss of interest*: Decreased interest in activities, hobbies, or social interactions. 4. *Physical symptoms*: Fatigue, headaches, or digestive problems. Treatment Options 1. *Therapy*: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), or psychodynamic therapy. 2. *Medication*: Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics. 3. *Lifestyle changes*: Regular exercise, healthy diet, social support, and stress management. To be continue0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 324 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY - PLEASE READ:
TOPIC: IMPORTANT OF HYDRATION
Staying hydrated is crucial for our bodies to function properly. Water makes up about 60% of our body weight and plays a vital role in:
1. Regulating body temperature: Water helps to regulate our body temperature through sweating.
2. Transporting nutrients and oxygen: Water helps to transport nutrients and oxygen to our cells.
3. Removing waste products: Water helps to remove waste products from our bodies.
Tips for Staying Hydrated:
1. Drink plenty of water: Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day.
2. Eat hydrating foods: Include foods with high water content in your diet, such as fruits and vegetables.
3. Avoid sugary drinks: Limit your intake of sugary drinks that can dehydrate you.
Benefits of Proper Hydration:
1. Boosts energy: Staying hydrated can help boost your energy levels.
2. Improves skin health: Proper hydration can help improve skin health and reduce wrinkles.
3. Supports kidney function: Drinking enough water can help support kidney function.
Let's prioritize our health today by staying hydrated!HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY - PLEASE READ: TOPIC: IMPORTANT OF HYDRATION Staying hydrated is crucial for our bodies to function properly. Water makes up about 60% of our body weight and plays a vital role in: 1. Regulating body temperature: Water helps to regulate our body temperature through sweating. 2. Transporting nutrients and oxygen: Water helps to transport nutrients and oxygen to our cells. 3. Removing waste products: Water helps to remove waste products from our bodies. Tips for Staying Hydrated: 1. Drink plenty of water: Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day. 2. Eat hydrating foods: Include foods with high water content in your diet, such as fruits and vegetables. 3. Avoid sugary drinks: Limit your intake of sugary drinks that can dehydrate you. Benefits of Proper Hydration: 1. Boosts energy: Staying hydrated can help boost your energy levels. 2. Improves skin health: Proper hydration can help improve skin health and reduce wrinkles. 3. Supports kidney function: Drinking enough water can help support kidney function. Let's prioritize our health today by staying hydrated!0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 267 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
Menstrual health is a crucial aspect of women's health. Here are some key points:
Importance of Menstrual Health
1. Reproductive health: Menstruation is a natural part of reproductive health.
2. Hormonal balance: Menstruation is regulated by hormones, and irregularities can indicate hormonal imbalances.
3. Overall health: Menstrual health can impact overall physical and mental well-being.
Common Menstrual Issues
1. Dysmenorrhea: Painful periods, often accompanied by cramps, bloating, and mood changes.
2. Menstrual irregularities: Irregular periods, heavy or light bleeding, and changes in menstrual cycle length.
3. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): Physical and emotional symptoms experienced before menstruation.
Menstrual Hygiene
1. Sanitary products: Pads, tampons, menstrual cups, and period panties.
2. Hygiene practices: Regular changing of sanitary products, washing hands, and maintaining genital hygiene.
3. Disposal: Proper disposal of sanitary products.
Managing Menstrual Health
1. Tracking periods: Keeping track of menstrual cycles to anticipate and prepare for periods.
2. Pain management: Using pain relievers, heat therapy, or other methods to manage menstrual cramps.
3. Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress to alleviate menstrual symptoms.
Breaking the Stigma
1. Open conversations: Encouraging open discussions about menstruation to break the stigma.
2. Education: Providing accurate information about menstrual health to promote awareness and understanding.
3. Support: Offering support and resources for individuals experiencing menstrual-related issues.
By prioritizing menstrual health, women can better manage their symptoms, improve their overall well-being, and break the stigma surrounding menstruation.Menstrual health is a crucial aspect of women's health. Here are some key points: Importance of Menstrual Health 1. Reproductive health: Menstruation is a natural part of reproductive health. 2. Hormonal balance: Menstruation is regulated by hormones, and irregularities can indicate hormonal imbalances. 3. Overall health: Menstrual health can impact overall physical and mental well-being. Common Menstrual Issues 1. Dysmenorrhea: Painful periods, often accompanied by cramps, bloating, and mood changes. 2. Menstrual irregularities: Irregular periods, heavy or light bleeding, and changes in menstrual cycle length. 3. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): Physical and emotional symptoms experienced before menstruation. Menstrual Hygiene 1. Sanitary products: Pads, tampons, menstrual cups, and period panties. 2. Hygiene practices: Regular changing of sanitary products, washing hands, and maintaining genital hygiene. 3. Disposal: Proper disposal of sanitary products. Managing Menstrual Health 1. Tracking periods: Keeping track of menstrual cycles to anticipate and prepare for periods. 2. Pain management: Using pain relievers, heat therapy, or other methods to manage menstrual cramps. 3. Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress to alleviate menstrual symptoms. Breaking the Stigma 1. Open conversations: Encouraging open discussions about menstruation to break the stigma. 2. Education: Providing accurate information about menstrual health to promote awareness and understanding. 3. Support: Offering support and resources for individuals experiencing menstrual-related issues. By prioritizing menstrual health, women can better manage their symptoms, improve their overall well-being, and break the stigma surrounding menstruation.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 448 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – part 2
Stages of Diabetes
1. Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
2. Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
3. Type 2 Diabetes: A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion.
4. Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester.
Managing Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes
1. Healthy Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2. Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
3. Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Stress Management: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Medication and Monitoring
1. Medications: Adhere to prescribed medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin therapy.
2. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly check blood sugar levels to adjust diet, exercise, or medication.
3. Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor diabetes progression and adjust treatment plans.
Complications Prevention
1. Foot Care: Regularly inspect and care for your feet to prevent ulcers and infections.
2. Eye Care: Schedule regular eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy.
3. Kidney Care: Monitor kidney function and manage blood pressure to prevent kidney damage.
Additional Tips
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration.
2. Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
3. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about diabetes management and stay up-to-date with the latest research and treatment options.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – part 2 Stages of Diabetes 1. Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. 2. Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. 3. Type 2 Diabetes: A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. 4. Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. Managing Diabetes Lifestyle Changes 1. Healthy Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. 2. Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. 3. Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity. 4. Stress Management: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Medication and Monitoring 1. Medications: Adhere to prescribed medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin therapy. 2. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly check blood sugar levels to adjust diet, exercise, or medication. 3. Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor diabetes progression and adjust treatment plans. Complications Prevention 1. Foot Care: Regularly inspect and care for your feet to prevent ulcers and infections. 2. Eye Care: Schedule regular eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy. 3. Kidney Care: Monitor kidney function and manage blood pressure to prevent kidney damage. Additional Tips 1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration. 2. Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels. 3. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about diabetes management and stay up-to-date with the latest research and treatment options.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 587 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY (DIABETES) – part 1 - PLEASE READ AND COMMENT
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. It helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream to use for energy.
Here are the main types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- An autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Typically develops in childhood or adolescence.
- Requires insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion.
- Often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet.
- Can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester.
- Typically goes away after pregnancy, but women with gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults)
- A form of type 1 diabetes that develops in adults.
- Often mistaken for type 2 diabetes, but requires insulin therapy.
5. MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young)
- A rare form of diabetes caused by genetic mutations.
- Typically develops in young adulthood.
6. Secondary Diabetes
- Develops as a result of another medical condition or treatment, such as pancreatitis, pancreatic surgery, or certain medications.
Each type of diabetes has its own unique characteristics and management strategies.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY (DIABETES) – part 1 - PLEASE READ AND COMMENT Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it produces. What is Insulin? Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. It helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream to use for energy. Here are the main types of diabetes: 1. Type 1 Diabetes - An autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. - Typically develops in childhood or adolescence. - Requires insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels. 2. Type 2 Diabetes - A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. - Often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. - Can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication. 3. Gestational Diabetes - Develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. - Typically goes away after pregnancy, but women with gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. 4. LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults) - A form of type 1 diabetes that develops in adults. - Often mistaken for type 2 diabetes, but requires insulin therapy. 5. MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young) - A rare form of diabetes caused by genetic mutations. - Typically develops in young adulthood. 6. Secondary Diabetes - Develops as a result of another medical condition or treatment, such as pancreatitis, pancreatic surgery, or certain medications. Each type of diabetes has its own unique characteristics and management strategies.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 382 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HERE ARE SOME ADDITIONAL DETAILS ABOUT DATE SEED OIL
Uses
1. Cosmetics: Date seed oil can be used in skincare products, such as moisturizers, creams, and serums, due to its antioxidant and moisturizing properties.
2. Haircare: Date seed oil can be used to nourish and condition hair, promoting healthy hair growth.
3. Culinary: Date seed oil can be used as a cooking oil, adding a unique flavor to dishes.
4. Pharmaceuticals: Date seed oil may have potential health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health.
Benefits
1. Rich in fatty acids: Date seed oil is rich in fatty acids, such as oleic and linoleic acid, which can help nourish and moisturize the skin.
2. Antioxidant properties: Date seed oil contains antioxidants, which can help protect against cell damage and oxidative stress.
3. Anti-inflammatory properties: Date seed oil may have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Production
1. Sustainable: Date seed oil production can be a sustainable way to utilize date seeds, which are often discarded.
2. Economic benefits: Date seed oil production can provide economic benefits for date farmers and producers.
Research
1. Nutritional content: Research has shown that date seed oil is rich in nutrients, including fatty acids and antioxidants.
2. Potential health benefits: Studies have suggested that date seed oil may have potential health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health.HERE ARE SOME ADDITIONAL DETAILS ABOUT DATE SEED OIL Uses 1. Cosmetics: Date seed oil can be used in skincare products, such as moisturizers, creams, and serums, due to its antioxidant and moisturizing properties. 2. Haircare: Date seed oil can be used to nourish and condition hair, promoting healthy hair growth. 3. Culinary: Date seed oil can be used as a cooking oil, adding a unique flavor to dishes. 4. Pharmaceuticals: Date seed oil may have potential health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health. Benefits 1. Rich in fatty acids: Date seed oil is rich in fatty acids, such as oleic and linoleic acid, which can help nourish and moisturize the skin. 2. Antioxidant properties: Date seed oil contains antioxidants, which can help protect against cell damage and oxidative stress. 3. Anti-inflammatory properties: Date seed oil may have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Production 1. Sustainable: Date seed oil production can be a sustainable way to utilize date seeds, which are often discarded. 2. Economic benefits: Date seed oil production can provide economic benefits for date farmers and producers. Research 1. Nutritional content: Research has shown that date seed oil is rich in nutrients, including fatty acids and antioxidants. 2. Potential health benefits: Studies have suggested that date seed oil may have potential health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 353 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 226 Visualizações 0 Anterior
-
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - PLEASE READ AND COMMENT
Dates are a nutritious fruit that offers several health benefits due to their richness in:
Nutrients
1. Fiber: Supports digestive health and satiety.
2. Antioxidants: Protects against cell damage and oxidative stress.
3. Potassium: Helps regulate blood pressure and supports heart health.
4. Vitamins and minerals: Rich in vitamins B and K, as well as minerals like copper, manganese, and selenium.
Health Benefits
1. Supports digestive health: Fiber content can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
2. May help lower cholesterol: Soluble fiber can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
3. Supports bone health: Rich in minerals like copper, manganese, and selenium, which are essential for bone health.
4. May help regulate blood sugar: Fiber and antioxidants may help slow down sugar absorption and improve insulin sensitivity.
5. Supports heart health: Potassium content can help lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Other Benefits
1. May aid in weight management: Fiber content can help with satiety and weight loss.
2. Supports immune function: Antioxidants and other nutrients can help boost the immune system.
3. May improve cognitive function: Antioxidants and other nutrients may help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Overall, dates are a nutritious and healthy addition to a balanced diet.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY - PLEASE READ AND COMMENT Dates are a nutritious fruit that offers several health benefits due to their richness in: Nutrients 1. Fiber: Supports digestive health and satiety. 2. Antioxidants: Protects against cell damage and oxidative stress. 3. Potassium: Helps regulate blood pressure and supports heart health. 4. Vitamins and minerals: Rich in vitamins B and K, as well as minerals like copper, manganese, and selenium. Health Benefits 1. Supports digestive health: Fiber content can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. 2. May help lower cholesterol: Soluble fiber can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. 3. Supports bone health: Rich in minerals like copper, manganese, and selenium, which are essential for bone health. 4. May help regulate blood sugar: Fiber and antioxidants may help slow down sugar absorption and improve insulin sensitivity. 5. Supports heart health: Potassium content can help lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease. Other Benefits 1. May aid in weight management: Fiber content can help with satiety and weight loss. 2. Supports immune function: Antioxidants and other nutrients can help boost the immune system. 3. May improve cognitive function: Antioxidants and other nutrients may help protect against age-related cognitive decline. Overall, dates are a nutritious and healthy addition to a balanced diet.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 283 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
HERE'S A HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY:
Mental Health Matters
Taking care of your mental health is just as important as taking care of your physical health. Here are some tips to prioritize your mental well-being:
1. Practice self-care: Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
2. Stay connected: Nurture relationships with loved ones and build a support network.
3. Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate your mood.
4. Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help reduce stress and anxiety.
5. Seek help when needed: Don't hesitate to reach out to a mental health professional if you're struggling.
Take Care of Your Body
1. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
2. Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods.
3. Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity per day.
4. Get enough sleep: Prioritize rest and aim for 7-8 hours per night.
Prioritize Your Well-being
1. Take breaks: Give yourself time to rest and recharge.
2. Practice mindfulness: Focus on the present moment and let go of stress.
3. Stay positive: Cultivate a positive mindset and focus on solutions.
I hope this health talk inspires you to prioritize your well-being!
HERE'S A HEALTH TALK FOR THE DAY: Mental Health Matters Taking care of your mental health is just as important as taking care of your physical health. Here are some tips to prioritize your mental well-being: 1. Practice self-care: Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation. 2. Stay connected: Nurture relationships with loved ones and build a support network. 3. Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate your mood. 4. Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help reduce stress and anxiety. 5. Seek help when needed: Don't hesitate to reach out to a mental health professional if you're struggling. Take Care of Your Body 1. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. 2. Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods. 3. Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity per day. 4. Get enough sleep: Prioritize rest and aim for 7-8 hours per night. Prioritize Your Well-being 1. Take breaks: Give yourself time to rest and recharge. 2. Practice mindfulness: Focus on the present moment and let go of stress. 3. Stay positive: Cultivate a positive mindset and focus on solutions. I hope this health talk inspires you to prioritize your well-being!0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 521 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
The causes of breast milk discharge in women who are not pregnant:
Hormonal Imbalances
1. Prolactin imbalance: Elevated levels of prolactin, a hormone that stimulates milk production, can cause breast milk discharge.
2. Thyroid disorders: Certain thyroid conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge.
Medications
1. Hormonal birth control: Certain types of hormonal birth control, such as birth control pills or patches, can cause breast milk discharge.
2. Antidepressants: Some antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can cause breast milk discharge.
Medical Conditions
1. Galactorrhea: A condition characterized by excessive milk production, often caused by hormonal imbalances or certain medical conditions.
2. Pituitary gland problems: Certain conditions, such as a pituitary tumor, can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge.
3. Breast cysts or tumors: Benign or cancerous growths in the breast tissue can cause breast milk discharge.
Other Causes
1. Stress: Chronic stress can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge.
2. Breast stimulation: Frequent breast stimulation, such as through massage or nipple play, can cause breast milk discharge.
Symptoms
1. Spontaneous milk discharge: Milk discharge from the breast without any apparent cause.
2. Breast tenderness: Pain or discomfort in the breast tissue.
3. Nipple discharge: Discharge from the nipple, which may be clear, white, or yellowish in color.
Diagnosis
1. Physical exam: A healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to assess the breast tissue and nipple discharge.
2. Hormone level tests: Blood tests may be used to check for hormonal imbalances.
3. Imaging tests: Mammograms or ultrasounds may be used to evaluate the breast tissue.
Treatment
1. Hormonal treatments: Medications may be prescribed to regulate hormonal imbalances.
2. Medication adjustments: Adjusting or discontinuing certain medications may help alleviate symptoms.
3. Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to remove breast cysts or tumors.
If you're experiencing breast milk discharge and are not pregnant, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.The causes of breast milk discharge in women who are not pregnant: Hormonal Imbalances 1. Prolactin imbalance: Elevated levels of prolactin, a hormone that stimulates milk production, can cause breast milk discharge. 2. Thyroid disorders: Certain thyroid conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge. Medications 1. Hormonal birth control: Certain types of hormonal birth control, such as birth control pills or patches, can cause breast milk discharge. 2. Antidepressants: Some antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can cause breast milk discharge. Medical Conditions 1. Galactorrhea: A condition characterized by excessive milk production, often caused by hormonal imbalances or certain medical conditions. 2. Pituitary gland problems: Certain conditions, such as a pituitary tumor, can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge. 3. Breast cysts or tumors: Benign or cancerous growths in the breast tissue can cause breast milk discharge. Other Causes 1. Stress: Chronic stress can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to breast milk discharge. 2. Breast stimulation: Frequent breast stimulation, such as through massage or nipple play, can cause breast milk discharge. Symptoms 1. Spontaneous milk discharge: Milk discharge from the breast without any apparent cause. 2. Breast tenderness: Pain or discomfort in the breast tissue. 3. Nipple discharge: Discharge from the nipple, which may be clear, white, or yellowish in color. Diagnosis 1. Physical exam: A healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to assess the breast tissue and nipple discharge. 2. Hormone level tests: Blood tests may be used to check for hormonal imbalances. 3. Imaging tests: Mammograms or ultrasounds may be used to evaluate the breast tissue. Treatment 1. Hormonal treatments: Medications may be prescribed to regulate hormonal imbalances. 2. Medication adjustments: Adjusting or discontinuing certain medications may help alleviate symptoms. 3. Surgery: Surgery may be necessary to remove breast cysts or tumors. If you're experiencing breast milk discharge and are not pregnant, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 310 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
DONT IGNORE PLEASE READ
YOUR HEALTH IS WEALTH
WHAT IS POSTRATE CANCER
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that affects the prostate gland, a small walnut-sized gland located in the male reproductive system. The prostate gland produces fluid that helps nourish and protect sperm.
Types of Prostate Cancer
1. Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases.
2. Small cell carcinoma: A rare and aggressive type.
3. Sarcoma: A rare type that originates in the connective tissue.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 50.
2. Family history: Having a first-degree relative (father or brother) with prostate cancer increases risk.
3. Genetics: Certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase risk.
4. Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
Symptoms
1. Urinary problems: Difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow.
2. Painful urination: Pain or burning sensation while urinating.
3. Blood in urine or semen: Presence of blood in urine or semen.
4. Pain in the back, hips, or chest: Pain or stiffness in these areas.
Diagnosis
1. Digital rectal exam (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate.
2. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: A blood test that measures PSA levels.
3. Biopsy: A procedure that removes tissue samples from the prostate.
Treatment Options
1. Active surveillance: Monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment.
2. Surgery: Removing the prostate gland (prostatectomy).
3. Radiation therapy: Using radiation to kill cancer cells.
4. Hormone therapy: Reducing testosterone levels to slow cancer growth.
Prevention and Early Detection
1. Regular screening: Discuss screening options with your doctor.
2. Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and eat a balanced diet.
3. Genetic testing: Consider genetic testing if you have a family history.
If you have concerns about prostate cancer, consult with your healthcare provider.DONT IGNORE PLEASE READ YOUR HEALTH IS WEALTH WHAT IS POSTRATE CANCER Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that affects the prostate gland, a small walnut-sized gland located in the male reproductive system. The prostate gland produces fluid that helps nourish and protect sperm. Types of Prostate Cancer 1. Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases. 2. Small cell carcinoma: A rare and aggressive type. 3. Sarcoma: A rare type that originates in the connective tissue. Causes and Risk Factors 1. Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 50. 2. Family history: Having a first-degree relative (father or brother) with prostate cancer increases risk. 3. Genetics: Certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase risk. 4. Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer. Symptoms 1. Urinary problems: Difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow. 2. Painful urination: Pain or burning sensation while urinating. 3. Blood in urine or semen: Presence of blood in urine or semen. 4. Pain in the back, hips, or chest: Pain or stiffness in these areas. Diagnosis 1. Digital rectal exam (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate. 2. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: A blood test that measures PSA levels. 3. Biopsy: A procedure that removes tissue samples from the prostate. Treatment Options 1. Active surveillance: Monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment. 2. Surgery: Removing the prostate gland (prostatectomy). 3. Radiation therapy: Using radiation to kill cancer cells. 4. Hormone therapy: Reducing testosterone levels to slow cancer growth. Prevention and Early Detection 1. Regular screening: Discuss screening options with your doctor. 2. Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and eat a balanced diet. 3. Genetic testing: Consider genetic testing if you have a family history. If you have concerns about prostate cancer, consult with your healthcare provider.0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 479 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
Here's a safety tip for today:
Safety Tip
Stay Aware of Your Surroundings
When out and about, make sure to stay alert and aware of your surroundings. This includes:
1. Watching for potential hazards: Be mindful of your environment, including uneven sidewalks, construction zones, and other obstacles.
2. Keeping valuables secure: Keep your belongings close and secure, especially in crowded areas or public transportation.
3. Being cautious with strangers: Be cautious when interacting with strangers, and avoid sharing personal information or accepting rides from unknown individuals.
Additional Tips
1. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay energized and focused.
2. Take breaks: Take regular breaks to rest and recharge, especially if you're engaging in physical activity.
3. Stay informed: Stay up-to-date with local news and weather forecasts to plan your day accordingly.
By following these tips, you can help ensure a safe and enjoyable day!Here's a safety tip for today: Safety Tip Stay Aware of Your Surroundings When out and about, make sure to stay alert and aware of your surroundings. This includes: 1. Watching for potential hazards: Be mindful of your environment, including uneven sidewalks, construction zones, and other obstacles. 2. Keeping valuables secure: Keep your belongings close and secure, especially in crowded areas or public transportation. 3. Being cautious with strangers: Be cautious when interacting with strangers, and avoid sharing personal information or accepting rides from unknown individuals. Additional Tips 1. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay energized and focused. 2. Take breaks: Take regular breaks to rest and recharge, especially if you're engaging in physical activity. 3. Stay informed: Stay up-to-date with local news and weather forecasts to plan your day accordingly. By following these tips, you can help ensure a safe and enjoyable day!0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 360 Visualizações 0 Anterior -
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 249 Visualizações 2 0 Anterior
-
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 376 Visualizações 0 Anterior1

-
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 349 Visualizações 0 Anterior1

-
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 340 Visualizações 0 Anterior1

-
0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 255 Visualizações 1 0 Anterior1

Mais Stories