HEALTH TALK FOR TODAT – BREAST CANCER (Please Read & Share)
Breast Cancer Awareness
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the breast tissue. It's one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
Key Facts:
1. Risk Factors: Family history, genetics, age, radiation exposure, and hormonal factors.
2. Symptoms: Lump or thickening in the breast, change in breast shape or size, nipple discharge or pain.
3. Screening: Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams.
4. Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Prevention and Early Detection:
1. Get screened regularly
2. Know your breast health
3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight)
4. Be aware of family history
Types of Breast Cancer:
1. Invasive ductal carcinoma: Begins in milk ducts and spreads to surrounding tissue.
2. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Starts in lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads.
3. Triple-negative breast cancer: Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors.
4. HER2-positive breast cancer: Has an overexpression of HER2 protein.
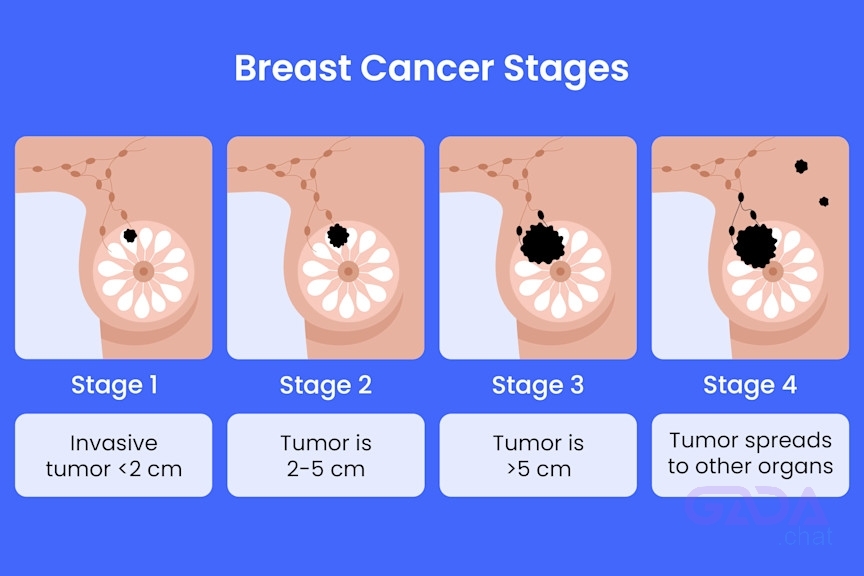
Stages of Breast Cancer:
1. Stage 0: Abnormal cells in breast tissue (non-invasive).
2. Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm) confined to breast tissue.
3. Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer in lymph nodes.
4. Stage III: Large tumor (over 5 cm) or extensive lymph node involvement.
5. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic).
Treatment Options:
1. Surgery: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast-conserving surgery.
2. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
3. Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells.
4. Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone receptors.
5. Targeted therapy: Medications targeting specific cancer cell proteins.
Support and Resources:
1. Breast cancer support groups
2. Oncology teams (doctors, nurses, social workers)
3. Online resources (American Cancer Society, National Breast Cancer Foundation)
4. Local cancer organizations
Let's Take Action:
1. Schedule a mammogram or clinical breast exam.
2. Practice breast self-awareness.
3. Support loved ones affected by breast cancer.
Remember: Early detection saves lives. Let's prioritize breast health and support those affected by breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Awareness
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the breast tissue. It's one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
Key Facts:
1. Risk Factors: Family history, genetics, age, radiation exposure, and hormonal factors.
2. Symptoms: Lump or thickening in the breast, change in breast shape or size, nipple discharge or pain.
3. Screening: Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams.
4. Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Prevention and Early Detection:
1. Get screened regularly
2. Know your breast health
3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight)
4. Be aware of family history
Types of Breast Cancer:
1. Invasive ductal carcinoma: Begins in milk ducts and spreads to surrounding tissue.
2. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Starts in lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads.
3. Triple-negative breast cancer: Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors.
4. HER2-positive breast cancer: Has an overexpression of HER2 protein.
Stages of Breast Cancer:
1. Stage 0: Abnormal cells in breast tissue (non-invasive).
2. Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm) confined to breast tissue.
3. Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer in lymph nodes.
4. Stage III: Large tumor (over 5 cm) or extensive lymph node involvement.
5. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic).
Treatment Options:
1. Surgery: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast-conserving surgery.
2. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
3. Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells.
4. Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone receptors.
5. Targeted therapy: Medications targeting specific cancer cell proteins.
Support and Resources:
1. Breast cancer support groups
2. Oncology teams (doctors, nurses, social workers)
3. Online resources (American Cancer Society, National Breast Cancer Foundation)
4. Local cancer organizations
Let's Take Action:
1. Schedule a mammogram or clinical breast exam.
2. Practice breast self-awareness.
3. Support loved ones affected by breast cancer.
Remember: Early detection saves lives. Let's prioritize breast health and support those affected by breast cancer.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAT – BREAST CANCER (Please Read & Share)
Breast Cancer Awareness
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the breast tissue. It's one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
Key Facts:
1. Risk Factors: Family history, genetics, age, radiation exposure, and hormonal factors.
2. Symptoms: Lump or thickening in the breast, change in breast shape or size, nipple discharge or pain.
3. Screening: Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams.
4. Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
Prevention and Early Detection:
1. Get screened regularly
2. Know your breast health
3. Maintain a healthy lifestyle (exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight)
4. Be aware of family history
Types of Breast Cancer:
1. Invasive ductal carcinoma: Begins in milk ducts and spreads to surrounding tissue.
2. Invasive lobular carcinoma: Starts in lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads.
3. Triple-negative breast cancer: Lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors.
4. HER2-positive breast cancer: Has an overexpression of HER2 protein.
Stages of Breast Cancer:
1. Stage 0: Abnormal cells in breast tissue (non-invasive).
2. Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm) confined to breast tissue.
3. Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer in lymph nodes.
4. Stage III: Large tumor (over 5 cm) or extensive lymph node involvement.
5. Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic).
Treatment Options:
1. Surgery: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, or breast-conserving surgery.
2. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
3. Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells.
4. Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone receptors.
5. Targeted therapy: Medications targeting specific cancer cell proteins.
Support and Resources:
1. Breast cancer support groups
2. Oncology teams (doctors, nurses, social workers)
3. Online resources (American Cancer Society, National Breast Cancer Foundation)
4. Local cancer organizations
Let's Take Action:
1. Schedule a mammogram or clinical breast exam.
2. Practice breast self-awareness.
3. Support loved ones affected by breast cancer.
Remember: Early detection saves lives. Let's prioritize breast health and support those affected by breast cancer.
0 Comments
0 Shares
334 Views
0 Reviews