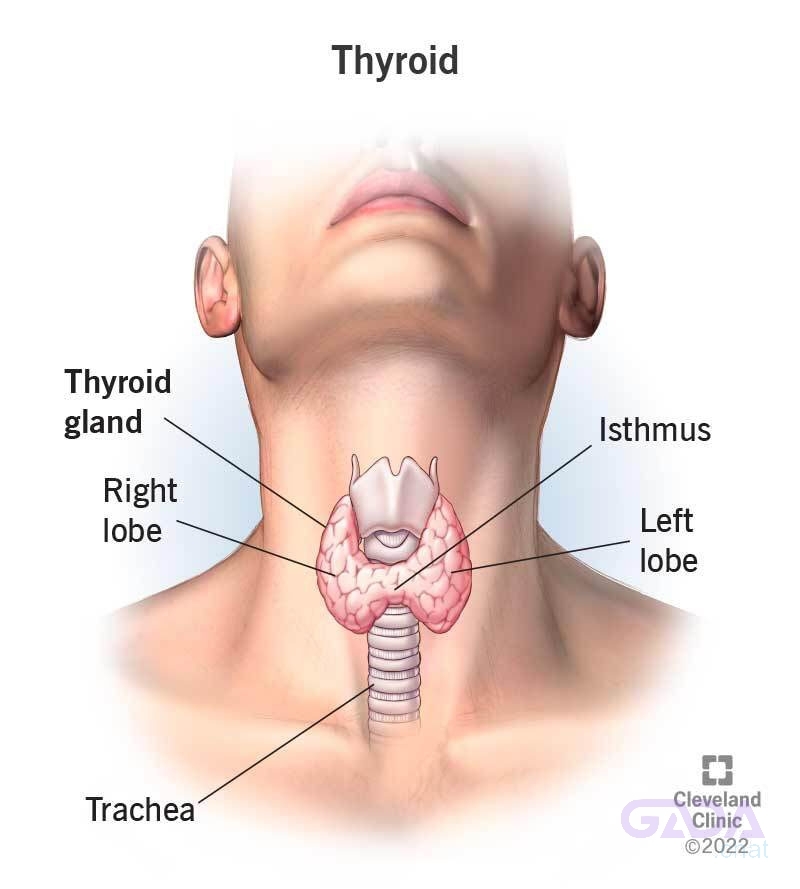
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share)
Part 2
If the thyroid gland is removed, either partially or entirely, it can have significant effects on the body.
Effects of Thyroid Removal
1. Hormone regulation: The body will no longer be able to produce thyroid hormones on its own.
2. Medication dependency: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate your metabolism.
3. Metabolic changes: Your metabolism may slow down, potentially leading to weight gain.
4. Energy levels: You may experience fatigue, weakness, or lethargy.
Types of Thyroid Removal
1. Partial thyroidectomy: Removing part of the thyroid gland.
2. Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire thyroid gland.
Post-Surgery Care
1. Medication management: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication as prescribed.
2. Regular check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
3. Lifestyle adjustments: You may need to make dietary changes or adjust your exercise routine.
Potential Complications
1. Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, which can be managed with medication.
2. Voice changes: Temporary or permanent changes to your voice.
3. Calcium levels: Potential impact on calcium levels in the body.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper medication management and care, many people can lead normal lives after thyroid removal surgery
THYROID CANCER is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating growth and metabolism.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
1. Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common type, often slow-growing.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, can spread to bones and lungs.
3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Rare, often linked to genetic mutations.
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Rare, aggressive, and fast-growing.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetic mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic mutations.
2. Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood.
3. Family history: Family history of thyroid cancer.
Symptoms
1. Neck lump: A lump or swelling in the neck.
2. Voice changes: Hoarseness or voice changes.
3. Swallowing difficulties: Difficulty swallowing.
4. Neck pain: Pain in the neck.
Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to diagnose cancer.
2. Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
3. Radioactive iodine therapy: Treatment to destroy remaining cancer cells.
4. Thyroid hormone replacement: Medication to replace thyroid hormones.
Prognosis
Thyroid cancer has a high cure rate, especially if detected early. The prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer.
Part 2
If the thyroid gland is removed, either partially or entirely, it can have significant effects on the body.
Effects of Thyroid Removal
1. Hormone regulation: The body will no longer be able to produce thyroid hormones on its own.
2. Medication dependency: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate your metabolism.
3. Metabolic changes: Your metabolism may slow down, potentially leading to weight gain.
4. Energy levels: You may experience fatigue, weakness, or lethargy.
Types of Thyroid Removal
1. Partial thyroidectomy: Removing part of the thyroid gland.
2. Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire thyroid gland.
Post-Surgery Care
1. Medication management: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication as prescribed.
2. Regular check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
3. Lifestyle adjustments: You may need to make dietary changes or adjust your exercise routine.
Potential Complications
1. Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, which can be managed with medication.
2. Voice changes: Temporary or permanent changes to your voice.
3. Calcium levels: Potential impact on calcium levels in the body.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper medication management and care, many people can lead normal lives after thyroid removal surgery
THYROID CANCER is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating growth and metabolism.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
1. Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common type, often slow-growing.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, can spread to bones and lungs.
3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Rare, often linked to genetic mutations.
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Rare, aggressive, and fast-growing.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetic mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic mutations.
2. Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood.
3. Family history: Family history of thyroid cancer.
Symptoms
1. Neck lump: A lump or swelling in the neck.
2. Voice changes: Hoarseness or voice changes.
3. Swallowing difficulties: Difficulty swallowing.
4. Neck pain: Pain in the neck.
Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to diagnose cancer.
2. Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
3. Radioactive iodine therapy: Treatment to destroy remaining cancer cells.
4. Thyroid hormone replacement: Medication to replace thyroid hormones.
Prognosis
Thyroid cancer has a high cure rate, especially if detected early. The prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer.
HEALTH TALK FOR TODAY – THYROID GLAND (Please Read & Share)
Part 2
If the thyroid gland is removed, either partially or entirely, it can have significant effects on the body.
Effects of Thyroid Removal
1. Hormone regulation: The body will no longer be able to produce thyroid hormones on its own.
2. Medication dependency: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate your metabolism.
3. Metabolic changes: Your metabolism may slow down, potentially leading to weight gain.
4. Energy levels: You may experience fatigue, weakness, or lethargy.
Types of Thyroid Removal
1. Partial thyroidectomy: Removing part of the thyroid gland.
2. Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire thyroid gland.
Post-Surgery Care
1. Medication management: You'll need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication as prescribed.
2. Regular check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
3. Lifestyle adjustments: You may need to make dietary changes or adjust your exercise routine.
Potential Complications
1. Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid, which can be managed with medication.
2. Voice changes: Temporary or permanent changes to your voice.
3. Calcium levels: Potential impact on calcium levels in the body.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper medication management and care, many people can lead normal lives after thyroid removal surgery
THYROID CANCER is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, a small gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating growth and metabolism.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
1. Papillary thyroid cancer: Most common type, often slow-growing.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer: Less common, can spread to bones and lungs.
3. Medullary thyroid cancer: Rare, often linked to genetic mutations.
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Rare, aggressive, and fast-growing.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetic mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic mutations.
2. Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood.
3. Family history: Family history of thyroid cancer.
Symptoms
1. Neck lump: A lump or swelling in the neck.
2. Voice changes: Hoarseness or voice changes.
3. Swallowing difficulties: Difficulty swallowing.
4. Neck pain: Pain in the neck.
Diagnosis and Treatment
1. Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to diagnose cancer.
2. Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy).
3. Radioactive iodine therapy: Treatment to destroy remaining cancer cells.
4. Thyroid hormone replacement: Medication to replace thyroid hormones.
Prognosis
Thyroid cancer has a high cure rate, especially if detected early. The prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer.
0 Yorumlar
0 hisse senetleri
231 Views
0 önizleme