TOPIC:
CONSEQUENCES OF GENDER BASED VIOLENCE
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) has severe and long-lasting consequences for individuals, families, and communities. Some potential consequences include:
Physical Consequences:
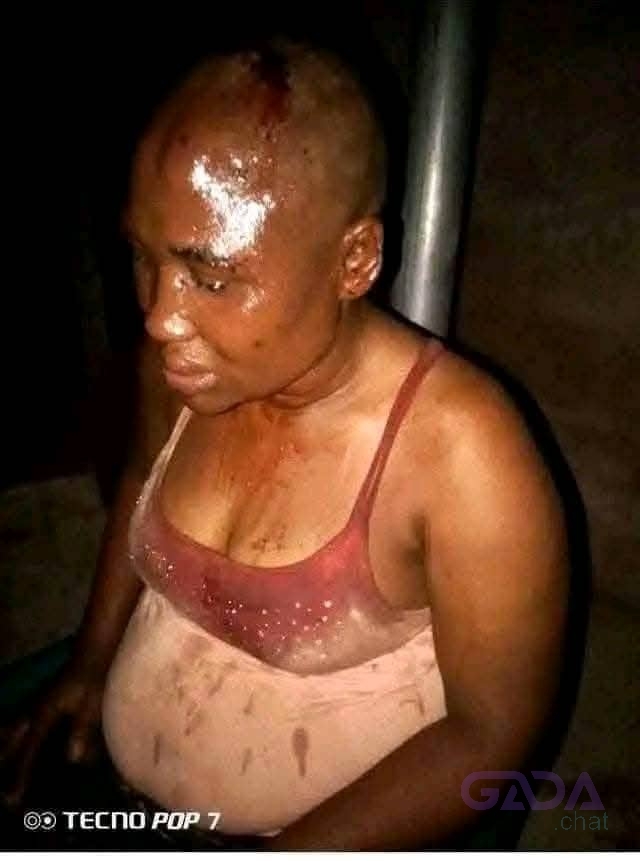
1. Injuries: Physical harm, bruises, cuts, broken bones, and other injuries.
2. Long-term health problems: Chronic pain, disability, and increased risk of health issues.
3. Death: Homicide, femicide, or suicide.
Emotional and Psychological Consequences:
1. Trauma: Emotional distress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
2. Depression: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
3. Low self-esteem: Negative impact on self-worth and self-perception.
4. Fear and anxiety: Constant fear and anxiety.
Social and Economic Consequences:
1. Social isolation: Withdrawal from social activities and relationships.
2. Economic instability: Loss of income, employment, or financial stability.
3. Strained relationships: Conflict with family, friends, or romantic partners.
4. Limited access to education and employment: Barriers to opportunities.
Consequences for Children:
1. Witnessing violence: Emotional trauma and impact on development.
2. Increased risk of abuse: Children may be more vulnerable to abuse.
3. Behavioral problems: Increased risk of behavioral issues or mental health problems.
Consequences for Communities:
1. Perpetuation of violence: Normalization of violence and abuse.
2. Social and economic costs: Increased healthcare, legal, and social services costs.
3. Community trauma: Collective trauma and impact on community well-being.
Breaking the Cycle:
1. Support services: Access to counseling, healthcare, and support services.
2. Education and awareness: Raising awareness about GBV and promoting healthy relationships.
3. Community engagement: Engaging communities in prevention and response efforts.
4. Policy and legislation: Strengthening laws and policies to protect survivors and hold perpetrators accountable.
CONSEQUENCES OF GENDER BASED VIOLENCE
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) has severe and long-lasting consequences for individuals, families, and communities. Some potential consequences include:
Physical Consequences:
1. Injuries: Physical harm, bruises, cuts, broken bones, and other injuries.
2. Long-term health problems: Chronic pain, disability, and increased risk of health issues.
3. Death: Homicide, femicide, or suicide.
Emotional and Psychological Consequences:
1. Trauma: Emotional distress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
2. Depression: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
3. Low self-esteem: Negative impact on self-worth and self-perception.
4. Fear and anxiety: Constant fear and anxiety.
Social and Economic Consequences:
1. Social isolation: Withdrawal from social activities and relationships.
2. Economic instability: Loss of income, employment, or financial stability.
3. Strained relationships: Conflict with family, friends, or romantic partners.
4. Limited access to education and employment: Barriers to opportunities.
Consequences for Children:
1. Witnessing violence: Emotional trauma and impact on development.
2. Increased risk of abuse: Children may be more vulnerable to abuse.
3. Behavioral problems: Increased risk of behavioral issues or mental health problems.
Consequences for Communities:
1. Perpetuation of violence: Normalization of violence and abuse.
2. Social and economic costs: Increased healthcare, legal, and social services costs.
3. Community trauma: Collective trauma and impact on community well-being.
Breaking the Cycle:
1. Support services: Access to counseling, healthcare, and support services.
2. Education and awareness: Raising awareness about GBV and promoting healthy relationships.
3. Community engagement: Engaging communities in prevention and response efforts.
4. Policy and legislation: Strengthening laws and policies to protect survivors and hold perpetrators accountable.
TOPIC:
CONSEQUENCES OF GENDER BASED VIOLENCE
Gender-Based Violence (GBV) has severe and long-lasting consequences for individuals, families, and communities. Some potential consequences include:
Physical Consequences:
1. Injuries: Physical harm, bruises, cuts, broken bones, and other injuries.
2. Long-term health problems: Chronic pain, disability, and increased risk of health issues.
3. Death: Homicide, femicide, or suicide.
Emotional and Psychological Consequences:
1. Trauma: Emotional distress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
2. Depression: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
3. Low self-esteem: Negative impact on self-worth and self-perception.
4. Fear and anxiety: Constant fear and anxiety.
Social and Economic Consequences:
1. Social isolation: Withdrawal from social activities and relationships.
2. Economic instability: Loss of income, employment, or financial stability.
3. Strained relationships: Conflict with family, friends, or romantic partners.
4. Limited access to education and employment: Barriers to opportunities.
Consequences for Children:
1. Witnessing violence: Emotional trauma and impact on development.
2. Increased risk of abuse: Children may be more vulnerable to abuse.
3. Behavioral problems: Increased risk of behavioral issues or mental health problems.
Consequences for Communities:
1. Perpetuation of violence: Normalization of violence and abuse.
2. Social and economic costs: Increased healthcare, legal, and social services costs.
3. Community trauma: Collective trauma and impact on community well-being.
Breaking the Cycle:
1. Support services: Access to counseling, healthcare, and support services.
2. Education and awareness: Raising awareness about GBV and promoting healthy relationships.
3. Community engagement: Engaging communities in prevention and response efforts.
4. Policy and legislation: Strengthening laws and policies to protect survivors and hold perpetrators accountable.
0 Comments
2 Shares
129 Views
0 Reviews