Acid Rain and Its Formation
What is Acid Rain?
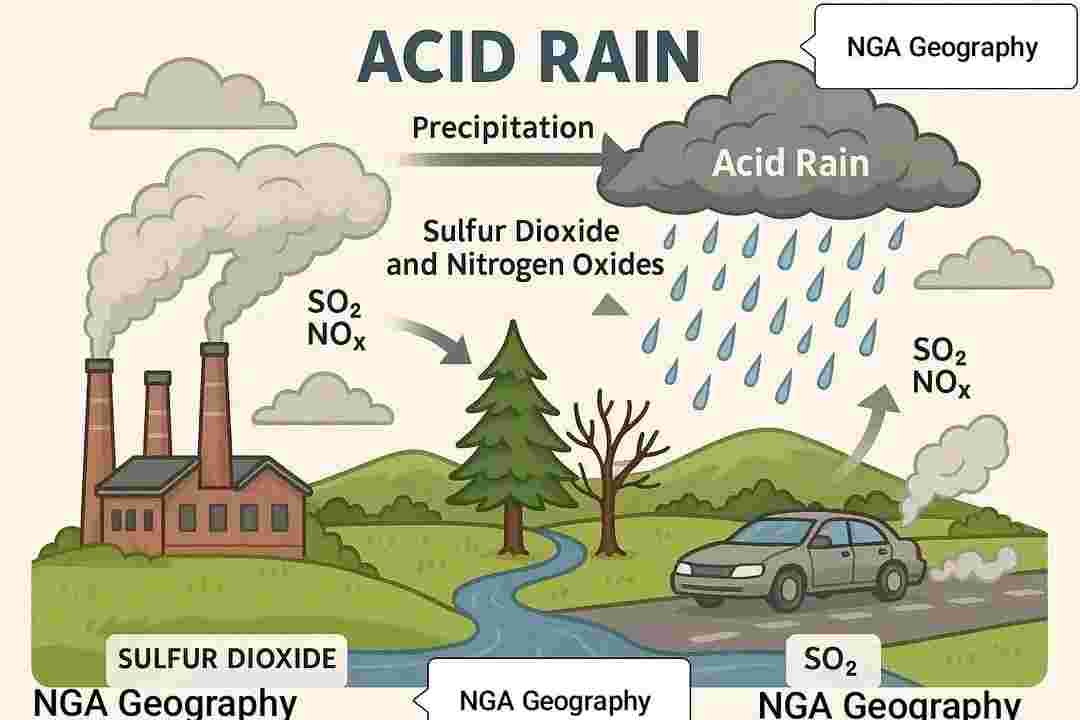
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation (rain, snow, fog, or dust) that has been made acidic due to the presence of certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It typically has a pH below 5.6 and can harm ecosystems, buildings, and human health.
Formation of Acid Rain:
1. Emission of Pollutants:
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ) are released into the atmosphere mainly from:
-Burning of fossil fuels in power plants and factories.
-Emissions from vehicles.
-Industrial processes such as smelting.
2. Chemical Reactions in the Atmosphere:
Once in the atmosphere, SO₂ and NOₓ react with water vapor (H₂O), oxygen (O₂), and other chemicals.
These reactions form:
-Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
-Nitric acid (HNO₃)
3. Acid Precipitation:
These acids mix with cloud moisture and fall to the ground as acid rain (or snow, fog, etc.).
Chemical Equations (Simplified):
-SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃ (sulfurous acid)
-2SO₂ + O₂ → 2SO₃; then SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄ (sulfuric acid)
-2NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₂ + HNO₃ (nitrous and nitric acids)
Environmental Effects:
- Soil and Water: Reduces pH, harming aquatic life and leaching nutrients from soil.
- Plants: Damages leaves, limits nutrient uptake.
- Buildings: Corrodes metal and erodes stone structures.
- Human Health: Can worsen respiratory problems when inhaled as fine particles.
Controlling acid rain involves reducing emissions of SO₂ and NOₓ through clean energy sources, emission filters (like scrubbers), and regulations such as the Clean Air Act.
Source~ NGA Geography
Credits to the rightful owner
Regards,
Dr. Adarsha Gowda
Food Expert
Chairperson/Dean/Head (Former)
Entrepreneurship, Startup & Consultancy
Dept of Food Science
Dept of Food Processing & Engineering.
What is Acid Rain?
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation (rain, snow, fog, or dust) that has been made acidic due to the presence of certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It typically has a pH below 5.6 and can harm ecosystems, buildings, and human health.
Formation of Acid Rain:
1. Emission of Pollutants:
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ) are released into the atmosphere mainly from:
-Burning of fossil fuels in power plants and factories.
-Emissions from vehicles.
-Industrial processes such as smelting.
2. Chemical Reactions in the Atmosphere:
Once in the atmosphere, SO₂ and NOₓ react with water vapor (H₂O), oxygen (O₂), and other chemicals.
These reactions form:
-Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
-Nitric acid (HNO₃)
3. Acid Precipitation:
These acids mix with cloud moisture and fall to the ground as acid rain (or snow, fog, etc.).
Chemical Equations (Simplified):
-SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃ (sulfurous acid)
-2SO₂ + O₂ → 2SO₃; then SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄ (sulfuric acid)
-2NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₂ + HNO₃ (nitrous and nitric acids)
Environmental Effects:
- Soil and Water: Reduces pH, harming aquatic life and leaching nutrients from soil.
- Plants: Damages leaves, limits nutrient uptake.
- Buildings: Corrodes metal and erodes stone structures.
- Human Health: Can worsen respiratory problems when inhaled as fine particles.
Controlling acid rain involves reducing emissions of SO₂ and NOₓ through clean energy sources, emission filters (like scrubbers), and regulations such as the Clean Air Act.
Source~ NGA Geography
Credits to the rightful owner
Regards,
Dr. Adarsha Gowda
Food Expert
Chairperson/Dean/Head (Former)
Entrepreneurship, Startup & Consultancy
Dept of Food Science
Dept of Food Processing & Engineering.
Acid Rain and Its Formation
What is Acid Rain?
Acid rain refers to any form of precipitation (rain, snow, fog, or dust) that has been made acidic due to the presence of certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It typically has a pH below 5.6 and can harm ecosystems, buildings, and human health.
Formation of Acid Rain:
1. Emission of Pollutants:
Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ) are released into the atmosphere mainly from:
-Burning of fossil fuels in power plants and factories.
-Emissions from vehicles.
-Industrial processes such as smelting.
2. Chemical Reactions in the Atmosphere:
Once in the atmosphere, SO₂ and NOₓ react with water vapor (H₂O), oxygen (O₂), and other chemicals.
These reactions form:
-Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
-Nitric acid (HNO₃)
3. Acid Precipitation:
These acids mix with cloud moisture and fall to the ground as acid rain (or snow, fog, etc.).
Chemical Equations (Simplified):
-SO₂ + H₂O → H₂SO₃ (sulfurous acid)
-2SO₂ + O₂ → 2SO₃; then SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄ (sulfuric acid)
-2NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₂ + HNO₃ (nitrous and nitric acids)
Environmental Effects:
- Soil and Water: Reduces pH, harming aquatic life and leaching nutrients from soil.
- Plants: Damages leaves, limits nutrient uptake.
- Buildings: Corrodes metal and erodes stone structures.
- Human Health: Can worsen respiratory problems when inhaled as fine particles.
Controlling acid rain involves reducing emissions of SO₂ and NOₓ through clean energy sources, emission filters (like scrubbers), and regulations such as the Clean Air Act.
Source~ NGA Geography
Credits to the rightful owner
Regards,
Dr. Adarsha Gowda
Food Expert
Chairperson/Dean/Head (Former)
Entrepreneurship, Startup & Consultancy
Dept of Food Science
Dept of Food Processing & Engineering.
💫